Hysterosalpingography (HSG): What is Hysterosalpingography (HSG)?
Diagnostic imaging is vital in women’s health, focusing on reproductive issues. Hysterosalpingography is a key tool, giving insights into the female reproductive system. This method is critical for examining the uterus and fallopian tubes. It aids in diagnosing and treating infertility and other reproductive health problems.
HSG offers a detailed view of reproductive anatomy. This clarity helps doctors create effective treatment plans. It significantly improves patient outcomes. HSG is a specialized imaging technique that offers deep insights into the female reproductive system. It’s used to check the uterine cavity’s shape and the fallopian tubes’ openness.
Definition and Basic Concept
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) uses a contrast agent and X-ray imaging to see inside the uterus and fallopian tubes. It’s often done in a radiology department or a specialist’s office. A small amount of contrast material is injected through the cervix into the uterine cavity. X-ray images are then taken to watch the contrast flow.
The core idea of HSG is its ability to give clear images of reproductive organs. This helps healthcare providers spot any abnormalities or blockages.
The Role of HSG in Reproductive Health
Hysterosalpingography is key in assessing reproductive health, mainly for those facing infertility or recurrent miscarriages. It offers detailed images of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. This helps diagnose issues like tubal blockages, uterine abnormalities, and other fertility-affecting conditions.
Understanding HSG’s role in reproductive health is vital for women trying to conceive or facing fertility issues. It’s a critical diagnostic tool that guides further treatment decisions.
The History and Evolution of Hysterosalpingography
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) has seen major changes from its start. It was initially designed to help diagnose reproductive problems. Now, it’s a key tool in gynecology.
Early Development of HSG
The early days of HSG go back to the early 20th century. It was first used to look at the uterus and fallopian tubes. The first methods used basic contrast materials and X-rays. As time went on, there were improvements:
- Refinements in contrast agents to reduce side effects and improve image quality
- Advancements in X-ray technology to reduce radiation exposure
- Development of more sophisticated catheter designs for easier and more comfortable procedures
These changes set the stage for today’s HSG practices.
Modern Advancements in HSG Technology
Recent years have brought big changes to HSG technology. These changes have improved both the diagnostic power and the patient experience. Some key developments include:
- Digital X-ray imaging, allowing for real-time imaging and improved diagnostic accuracy
- Advanced contrast materials with better safety profiles and image quality
- Integration of HSG with other diagnostic modalities, such as ultrasound, for a more complete evaluation
These modern advancements have made HSG a more effective and safer diagnostic tool. They’ve helped keep HSG relevant in reproductive medicine.
Why is an HSG Performed?
An HSG is a key diagnostic tool for assessing female fertility and reproductive health. It offers vital insights into the fallopian tubes and uterus. This is essential for diagnosing and treating various reproductive health issues.
Fertility Investigation
One main reason for an HSG is to explore fertility issues in women. It examines the fallopian tubes and uterus. Healthcare providers can spot blockages or abnormalities that might cause infertility.
This insight is critical for creating an effective treatment plan. It might include surgery, fertility medications, or other reproductive technologies.
Evaluation of Tubal Patency
HSG is also great for checking the fallopian tubes’ patency. A contrast material is introduced into the uterus and tubes. This allows for the visualization of any blockages or abnormalities.
Assessing tubal patency helps healthcare providers see if issues prevent fertilization or cause other reproductive problems.
Uterine Abnormality Assessment
HSG also helps identify uterine abnormalities, like structural defects or lesions. This information is vital for understanding reproductive issues and developing a treatment plan.
By examining the uterus’s shape and condition, healthcare providers can better understand a patient’s reproductive health. They can then provide targeted care.
Medical Conditions Diagnosed Through HSG
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is a key diagnostic tool for identifying various medical conditions affecting female reproductive health. It offers essential insights into the structure and function of the female reproductive system, focusing on the fallopian tubes and uterus.
Fallopian Tube Blockages
One of the primary uses of HSG is to diagnose blockages in the fallopian tubes. These blockages can significantly impact fertility.
Proximal Blockages
Proximal blockages occur near the uterus and can be caused by conditions such as tubal spasm or anatomical abnormalities. Accurate diagnosis is critical for determining the appropriate treatment.
Distal Blockages
Distal blockages occur at the end of the fallopian tube, near the ovary. These blockages can be due to conditions like hydrosalpinx, where the tube becomes filled with fluid.
Uterine Abnormalities
HSG is also effective in identifying various uterine abnormalities that can affect reproductive health.
Congenital Malformations
Congenital malformations, such as a unicornuate or bicornuate uterus, can be detected through HSG. These conditions can impact fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
Acquired Abnormalities
Acquired abnormalities, including intrauterine adhesions and fibroids, can also be diagnosed using HSG. These conditions can cause symptoms like pelvic pain and heavy menstrual bleeding.
Other Detectable Conditions
In addition to fallopian tube blockages and uterine abnormalities, HSG can help identify other conditions that may affect reproductive health. These include:
- Tubal damage or scarring
- Peritubal adhesions
- Abnormalities of the uterine cavity
By diagnosing these conditions, healthcare providers can develop appropriate treatment plans to address the underlying causes of infertility or other reproductive issues.
When to Schedule Your Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
Scheduling HSG at the right time in your menstrual cycle is vital for its success. The timing of HSG greatly influences the test’s accuracy. It’s important to schedule it when it can offer the most insightful information about your reproductive system.
Optimal Timing in the Menstrual Cycle
The best time for an HSG is between days 7 and 14 of your menstrual cycle. This timing reduces the risk of an early pregnancy and ensures the uterine lining is not too thick. Such conditions can impact the test’s accuracy.
It’s important to avoid scheduling an HSG during active menstruation. This can cause discomfort and increase the risk of infection. Also, the test should be done before ovulation to protect a newly conceived embryo.
Coordinating with Fertility Treatments
For women undergoing fertility treatments, coordinating HSG timing with their treatment cycle is essential. This ensures the procedure doesn’t disrupt the treatment and that the results are beneficial for planning the next steps in fertility care.
Working closely with a fertility specialist is critical to determine the best HSG timing within the broader fertility treatment plan. This collaboration enhances the diagnostic value of the HSG and supports the overall fertility treatment strategy.
Preparing for Your HSG Procedure
Getting ready for your HSG procedure involves several key steps. These steps are designed to make the experience as smooth and successful as possible. Understanding them can help ease any worries and make the process more comfortable for you.
Pre-Procedure Instructions
Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions before the HSG. These might include arriving at a certain time, bringing someone with you, or other details. It’s essential to follow these instructions closely to ensure the procedure goes smoothly.
- Arrive at the scheduled time
- Bring any required documents or insurance information
- Have a friend or family member accompany you
Medications and Dietary Restrictions
Your doctor will likely advise on medications and dietary restrictions before the HSG. This could mean avoiding certain foods or drinks, or stopping specific medications temporarily. Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re currently taking to avoid any interactions.
Mental and Emotional Preparation
Mental and emotional preparation is also key. Knowing what to expect during the procedure can help reduce anxiety. Talk to your healthcare provider about any concerns and consider relaxation techniques like deep breathing to stay calm.
By following these guidelines and communicating openly with your healthcare provider, you can ensure you’re well-prepared for your HSG procedure.
What to Expect During an HSG Procedure
Understanding the HSG procedure can help alleviate anxiety and prepare you for the experience. This diagnostic test evaluates the shape of your uterus and whether your fallopian tubes are open or blocked.
Step-by-Step Process
The HSG procedure involves several steps, each designed to provide a clear picture of your reproductive health.
Initial Setup
The procedure begins with a speculum being inserted into your vagina to visualize your cervix. The cervix is then cleaned, and a catheter is gently inserted into the cervical canal.
Contrast Material Injection
A contrast material is injected through the catheter into your uterus. This material helps to outline the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes on X-ray images.
X-ray Imaging
X-ray images are taken as the contrast material fills your uterus and flows through your fallopian tubes. These images help your doctor assess the patency of your tubes and the shape of your uterine cavity.
Duration and Sensation
The entire HSG procedure typically takes about 15 to 30 minutes. You may experience some discomfort during the procedure, similar to menstrual cramps.
Managing Discomfort
To manage discomfort, you can take deep breaths and try to relax. Some women also find it helpful to have a friend or family member present for support.
Communication with Medical Staff
It’s essential to communicate openly with your medical team about any pain or discomfort you’re experiencing. They can provide guidance and support throughout the procedure.
The Technology Behind Hysterosalpingography
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is a diagnostic procedure that uses advanced technology to examine the female reproductive system. It relies on X-ray imaging and contrast materials to provide critical insights. This technology is key to its effectiveness.
X-ray Imaging in HSG
X-ray imaging is essential in HSG. It allows healthcare providers to see the internal structures of the reproductive system. X-rays capture detailed images of the uterus and fallopian tubes. This helps identify any abnormalities or blockages.

Contrast Materials Used
Contrast materials are vital in HSG. They highlight the reproductive structures, making X-ray images clearer. There are two main types of contrast materials used in HSG.
Oil-Based vs. Water-Based Contrast
The choice between oil-based and water-based contrasts depends on several factors. These include the patient’s medical history and the procedure’s goals. Historically, oil-based contrasts were more common. But, water-based contrasts are now preferred due to their lower risk of complications.
Safety Profiles
Both oil-based and water-based contrasts have been studied for their safety. While generally safe, there are risks, such as allergic reactions and infection. Healthcare providers carefully consider these risks when choosing a contrast material.
Post-HSG Care and Recovery
Understanding the necessary steps for post-procedure care is key to a smooth recovery after an HSG. Proper care and recovery measures are vital to minimize side effects and ensure well-being.
Immediate Aftercare
Right after the HSG procedure, patients are told to rest for a short time. This helps the body recover from any discomfort or cramping that might occur.
Some common recommendations for immediate aftercare include:
- Resting for a few hours
- Avoiding strenuous activities
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers if necessary
When to Resume Normal Activities
Returning to normal activities after an HSG should be done gradually. It’s critical to follow the specific guidance from your healthcare provider.
Physical Activities
Patients are usually advised to avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous exercise for a few days after the procedure. Light activities can typically be resumed within 24 to 48 hours.
Sexual Activity
Regarding sexual activity, it’s generally recommended to wait a few days after the procedure to minimize the risk of infection. Your healthcare provider will give specific advice based on your individual situation.
Potential Risks and Complications of HSG
HSG is generally considered safe, but it’s vital to know the possible risks and complications. Like any medical tool, it can have side effects and complications. Patients should be informed about these before the procedure.
Common Side Effects
Most women experience minimal side effects after HSG. Common issues include:
- Mild cramping
- Spotting or light bleeding
- Dizziness
- Nausea
These side effects are usually short-lived and often resolve without medical help.
Rare but Serious Complications
Though rare, serious complications can occur. These include:
- Infection
- Allergic reactions to the contrast dye
- Damage to the fallopian tubes or uterus
- Intravasation of contrast material into the bloodstream
Discussing individual risk factors with a healthcare provider is essential.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s important to watch for signs of complications after HSG. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Heavy bleeding
- Fever or chills
- Signs of an allergic reaction
Being aware of these complications and knowing when to seek help can greatly improve outcomes.
Interpreting HSG Results
The outcome of an HSG test offers insights into the fallopian tubes and uterus’s condition. It’s vital to understand these results for diagnosing fertility issues and planning the next steps.
Normal Findings
Normal HSG results show the fallopian tubes are open and the uterus is normal. This means there are no major blockages or abnormalities in the reproductive system. Such findings suggest fertility issues are unlikely.
Abnormal Results and Their Meanings
Abnormal HSG results may indicate blocked fallopian tubes, uterine issues like fibroids or polyps, or other structural problems. These findings help healthcare providers pinpoint the causes of infertility or recurrent miscarriages.
Follow-up Recommendations
Based on HSG results, further actions might include diagnostic tests like laparoscopy or hysteroscopy, fertility treatments, or surgery. Healthcare providers will suggest the best next steps based on your specific situation.
HSG vs. Alternative Diagnostic Procedures
Diverse diagnostic methods like HSG, sonohysterography, laparoscopy, and hysteroscopy are employed to assess female reproductive health. Each method has its unique approach and outcomes. It’s critical for healthcare professionals to understand these differences to recommend the most fitting test for their patients.
Sonohysterography
Sonohysterography, or saline infusion sonography, employs ultrasound to examine the uterus’s interior. It involves filling the uterus with saline to enhance ultrasound clarity. This method is effective for spotting uterine anomalies like polyps, fibroids, and adhesions.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy offers a direct view of the pelvic organs, including the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and uterus. It involves small abdominal incisions for a laparoscope, a thin, lighted tube with a camera. Laparoscopy is the top choice for diagnosing endometriosis and tubal damage.
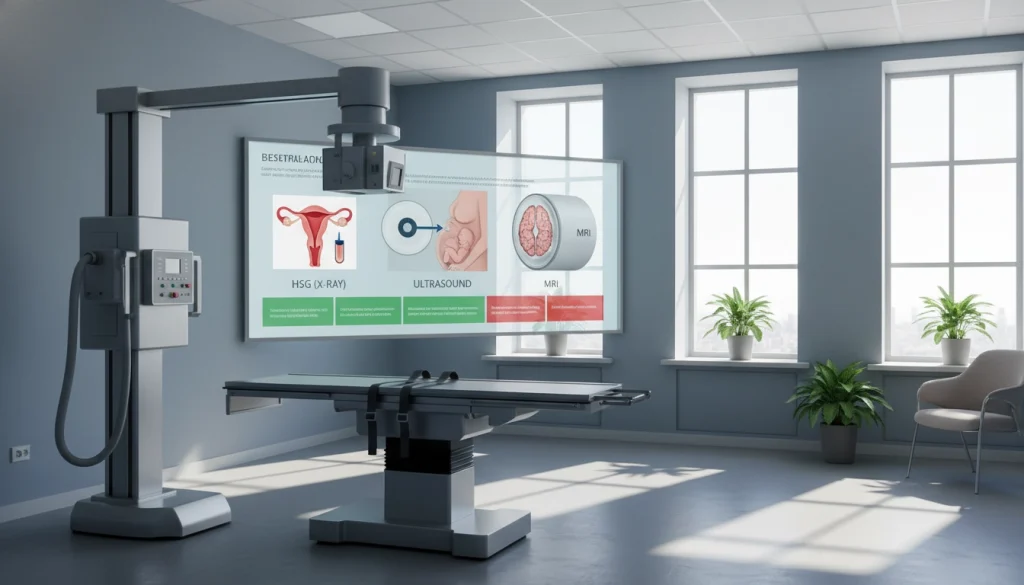

Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy allows for direct uterine cavity examination with a hysteroscope, a thin, flexible or rigid telescope. It serves both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, like removing polyps or fibroids. Hysteroscopy offers detailed uterine cavity insights and can be done in an office or as outpatient surgery.
Each diagnostic procedure has its indications, advantages, and limitations. The selection between them hinges on the patient’s condition, medical history, and suspected symptom cause.
Cost and Insurance Coverage for HSG in the United States
Understanding the costs of HSG is critical. The financial impact of an HSG procedure varies. This depends on location, healthcare provider, and insurance coverage.
Average Costs Without Insurance
The average cost of an HSG procedure without insurance is between $300 and $1,000. This range is due to differences in provider charges and the services included.
Insurance Coverage Options
Insurance can greatly reduce the cost of HSG. Most plans cover diagnostic procedures, including HSG, for fertility investigations.
Coverage Under Fertility Benefits
Many insurance plans include fertility benefits. These benefits often cover diagnostic tests like HSG. This can lessen the financial strain on those undergoing fertility treatments.
Coverage as Diagnostic Procedure
HSG is frequently covered as a diagnostic procedure. Coverage varies based on the plan and the procedure’s medical necessity.
- Check your insurance plan details for coverage.
- Understand the out-of-pocket costs associated with HSG.
- Discuss financial options with your healthcare provider.
The Therapeutic Effects of HSG
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) has gained significant attention for its therapeutic effects, mainly in boosting fertility. It goes beyond just diagnosing, potentially improving fertility outcomes for patients. This makes it a valuable tool in reproductive health.
Potential Fertility Enhancement
HSG’s ability to enhance fertility is a key aspect of its therapeutic benefits. Studies indicate that the procedure can clear minor blockages in the fallopian tubes. This could improve tubal patency and, in turn, fertility.
Scientific Evidence for Therapeutic Benefits
Scientific evidence supporting HSG’s therapeutic benefits is expanding. Research shows that it may not only diagnose but also treat certain fertility issues. For instance, minor tubal adhesions. Yet, more in-depth studies are required to fully grasp its therapeutic effects.
The therapeutic effects of HSG, with a focus on fertility enhancement, highlight its diverse benefits. As ongoing research sheds more light, HSG continues to be a critical asset in diagnosing and treating fertility-related issues.
Patient Experiences and Emotional Aspects of HSG
Understanding the emotional impact of HSG on patients is key to providing full care. The procedure, though diagnostic, can trigger different emotional responses in patients.
Common Emotional Responses
Patients undergoing HSG may feel anxious or apprehensive due to the procedure’s unknowns. Some might experience discomfort or pain, intensifying their emotional state.
A study revealed that many patients felt nervous before the procedure. Yet, this anxiety often subsided once the procedure started.
Coping Strategies and Support
Healthcare providers can offer various coping strategies to lessen emotional impact. These include pre-procedure counseling, relaxation techniques, and detailed explanations of the procedure.
Support from family and friends is also vital in helping patients deal with HSG’s emotional aspects. By recognizing these emotional aspects, healthcare providers can offer more complete care.
Making Informed Decisions About Hysterosalpingography
Understanding Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is key to informed fertility decisions. We’ve covered its definition, history, and procedure. We’ve also discussed its benefits and risks.
When thinking about HSG, consider your health needs and goals. Talk to your healthcare provider about your medical history and fertility aspirations. This will help decide if HSG is right for you.
Understanding HSG’s implications is vital. It can offer insights into your reproductive health and even therapeutic benefits. Being informed empowers you to actively manage your fertility journey.
Your decision to have HSG should be well-informed. Know its benefits and risks and how they apply to you. Empowering yourself with knowledge supports your reproductive health and well-being.
FAQ About Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
Q: What is Hysterosalpingography (HSG) used for?
A: HSG is a diagnostic tool used to check the uterine cavity’s shape and the fallopian tubes’ openness. It’s commonly used in fertility assessments.
Q: Is HSG a painful procedure?
A: Some women might feel mild to moderate discomfort or cramping during HSG. Yet, it’s generally not painful and is well-tolerated by most.
Q: How long does an HSG procedure take?
A: The HSG procedure itself usually lasts 15 to 30 minutes. But, the whole process, including preparation and recovery, can take longer.
Q: What are the risks associated with HSG?
A: Risks of HSG include infection and allergic reactions to the contrast material. There’s also a minimal risk of radiation exposure.
Q: Can HSG diagnose all types of fertility issues?
A: HSG mainly checks tubal patency and uterine abnormalities. It might not detect all fertility problems; other tests may be needed.
Q: How should I prepare for an HSG procedure?
A: To prepare for HSG, arrive with a full bladder and have someone with you. You might also take medication for discomfort.
Q: Can I resume normal activities after HSG?
A: Most women can go back to normal activities soon after HSG. But, it’s wise to avoid strenuous activities or sex for a bit.
Q: How is HSG different from other diagnostic fertility tests?
A: HSG uses X-ray imaging and contrast to assess the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. It’s different from tests like sonohysterography or laparoscopy.
Q: Will my insurance cover the cost of HSG?
A: Insurance coverage for HSG varies. It depends on the provider and your plan. Some cover it as a diagnostic or under fertility benefits.
Q: Can HSG have therapeutic effects on fertility?
A: Some studies suggest HSG might improve fertility chances. But, more research is needed to confirm this therapeutic effect.