Joint Diseases: Understanding Joint Anatomy and Function
Conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system can cause significant pain and limited mobility. Understanding these complex health issues is key to developing effective treatment plans. A wide range of conditions fall under the category of joint diseases, impacting the quality of life for millions. These conditions can result from various factors, including age, injury, or autoimmune responses.
Effective management of these conditions requires a holistic approach. This includes accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies. Grasping the details of joint anatomy and function is key to understanding joint diseases. Joints are complex structures that allow for movement and flexibility in our bodies.
Basic Joint Structure
A joint, or articulation, is where two or more bones meet. It consists of bones, cartilage, synovium, and ligaments. The synovium produces synovial fluid, which lubricates and nourishes the joint.
Types of Joints in the Human Body
The human body has different types of joints. Synovial joints, like the knee and elbow, have a space filled with synovial fluid. Cartilaginous joints are connected by cartilage, and fibrous joints are joined by dense tissue.
Normal Joint Mechanics
Normal joint mechanics involve the movement of bones, ligaments, and muscles working together. This balance ensures smooth, pain-free movement. Any disruption, like injury or disease, can cause joint dysfunction and diseases.
Overview of Joint Diseases
Joint diseases cover a wide range of conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system. These issues can greatly reduce an individual’s quality of life. They cause pain, stiffness, and limit mobility.
Definition and Classification
Joint diseases fall into several categories, including inflammatory, degenerative, metabolic, and infectious conditions. Common types include rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and gout. Knowing the classification is key for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Global Prevalence and Impact
The global prevalence of joint diseases is significant and growing. The World Health Organization reports millions worldwide suffer from arthritis and other joint conditions. This trend has major implications for public health and healthcare systems.
Economic Burden of Joint Disorders
The economic impact of joint diseases is substantial. It includes direct medical costs and indirect costs like lost productivity. In the United States, the annual cost of arthritis and joint diseases is in the hundreds of billions of dollars. Developing effective management and prevention strategies is vital to reduce this economic burden.
Common Types of Inflammatory Arthritis
Inflammatory arthritis includes a variety of chronic conditions marked by joint inflammation and pain. These conditions can greatly affect an individual’s quality of life. It’s essential to understand their characteristics and symptoms thoroughly.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder mainly affecting the hands and feet. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints. This leads to inflammation, pain, and potentially severe joint damage.
- Symptoms include symmetric joint pain and swelling.
- Morning stiffness is a common complaint.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is linked to psoriasis, a skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. This form of arthritis causes joint inflammation. It can lead to significant discomfort and disability.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis mainly affects the spine, though other joints can also be involved. It leads to chronic pain and stiffness. In severe cases, it can result in the fusion of vertebrae.
- Back pain and stiffness are hallmark symptoms.
- It can lead to reduced mobility and flexibility.
- Early treatment can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis refers to a group of arthritic conditions in children. It can cause joint inflammation, pain, and swelling. This can potentially affect growth and development.
- Symptoms can vary widely among affected children.
- Early diagnosis is critical for effective management.
- Treatment plans often involve a combination of medication and physical therapy.
Understanding these common types of inflammatory arthritis is key for diagnosis and treatment. Each condition has its unique characteristics. A tailored approach is necessary for effective management.
Degenerative Joint Conditions
Degenerative joint conditions include a variety of disorders affecting the joints. These issues are marked by the gradual wear down of cartilage and surrounding tissues. This leads to pain and a decrease in mobility.
These conditions are a major cause of disability globally. They not only impact the quality of life but also put a heavy burden on healthcare systems financially.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent form of degenerative joint disease. It mainly affects weight-bearing joints like the hips, knees, and spine. The breakdown of cartilage results in bone-on-bone contact, causing severe pain.
Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease impacts the spinal discs, causing back pain and limited mobility. It occurs as the discs lose hydration and height over time. This can lead to bulging or herniation.
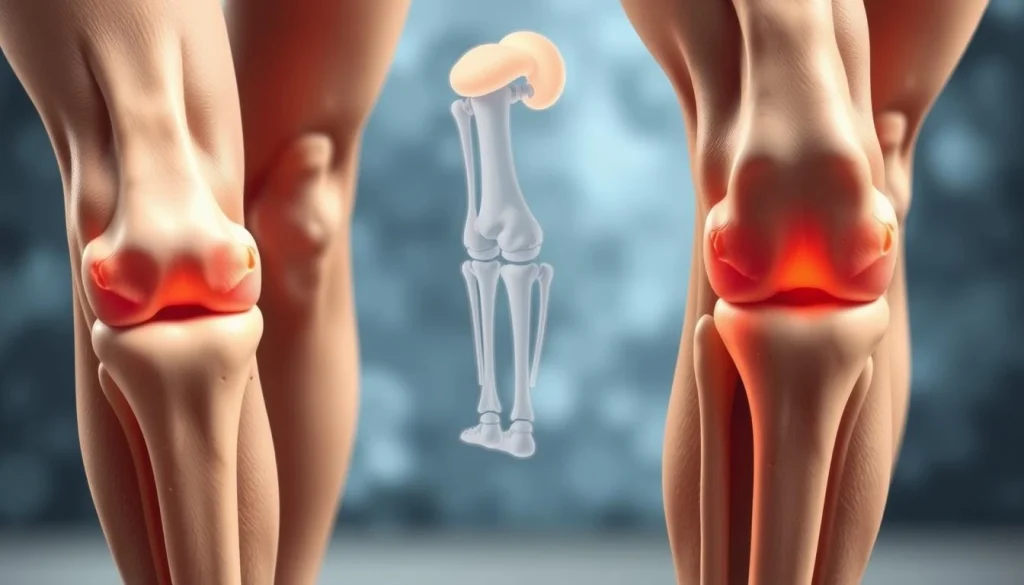
Age-Related Joint Changes
Age-related joint changes play a significant role in degenerative joint conditions. As people age, joints naturally wear down. This includes cartilage loss and changes in bone density, making them more prone to these conditions.
In conclusion, degenerative joint conditions require a multifaceted approach for management and treatment. It’s essential to understand the different types, such as osteoarthritis and degenerative disc disease, for effective care.
Metabolic and Crystal-Induced Joint Diseases
Metabolic and crystal-induced joint diseases are unique categories of joint disorders. They arise from the buildup of crystals or metabolic waste in joints. These conditions can cause severe pain, inflammation, and disability.
Gout
Gout is a metabolic joint disease caused by urate crystals in joints. It’s known for sudden, intense pain, redness, and swelling, often at the big toe’s base. Treatment aims to lower uric acid levels and ease symptoms.
Pseudogout (Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition)
Pseudogout, or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), involves calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals in joints. It can look like gout but needs different treatments and diagnostic methods.
Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis is a genetic disorder causing too much iron absorption and deposition in tissues, including joints. This leads to joint pain and degeneration. Early detection and treatment are key to avoiding permanent damage.
It’s vital to understand metabolic and crystal-induced joint diseases for proper diagnosis and treatment. Each condition has its own pathophysiology and treatment strategy. This underlines the need for accurate diagnosis.
Recognizing Joint Disease Symptoms
Joint disease symptoms vary widely, but understanding them is essential for managing the condition. Joint diseases include a range of disorders affecting the joints. These cause discomfort, pain, and limited mobility.
Pain Patterns and Characteristics
Pain is a primary symptom of joint diseases, providing insights into the underlying condition. The pain can be acute or chronic, sharp or dull. It may be localized to a specific joint or widespread.
Inflammatory arthritis often presents with morning stiffness and pain that improves with movement. On the other hand, osteoarthritis tends to cause pain that worsens with activity.
Swelling and Inflammation Signs
Swelling and inflammation are common signs of joint diseases, seen in inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. The affected joint may appear red, warm to the touch, and swollen due to fluid accumulation.
In some cases, swelling is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or fatigue. These indicate a systemic response.
Mobility and Function Changes
Joint diseases often lead to changes in mobility and function. Symptoms include stiffness, reduced range of motion, and difficulty performing daily activities. Patients may also experience a grinding or crunching sensation in the joints, known as crepitus.
Systemic Symptoms
Some joint diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis, can present with systemic symptoms. These include fever, fatigue, and weight loss. These symptoms indicate the disease is affecting the body beyond the joints.
Recognizing these systemic symptoms is critical for diagnosing and managing the underlying condition effectively.
Risk Factors for Developing Joint Diseases
Several key risk factors contribute to the likelihood of developing joint diseases. These include genetic, age-related, and lifestyle factors. Understanding these risk factors is essential for prevention, early diagnosis, and effective management of joint conditions.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic predisposition significantly influences the development of certain joint diseases. For example, individuals with a family history of rheumatoid arthritis are more likely to develop it. Specific genetic markers have been linked to an increased risk of various forms of arthritis.
Age-Related Changes
Age is a major risk factor for many joint diseases, such as osteoarthritis. As people age, the wear and tear on their joints increases. This leads to a higher risk of joint degeneration.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors, including obesity and smoking, significantly contribute to the risk of developing joint diseases. Obesity increases the stress on weight-bearing joints. Smoking can impair joint health and overall well-being.
Previous Joint Injuries
Previous joint injuries can also increase the risk of developing joint diseases, such as osteoarthritis. The trauma from an injury can initiate a degenerative process. This may lead to chronic joint problems over time.
By understanding these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps. They can mitigate their risk and maintain healthier joints throughout their lives.
Diagnostic Approaches for Joint Diseases
Clinicians use various strategies to diagnose and manage joint diseases. These include clinical evaluations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Accurate diagnosis is key to creating effective treatment plans and improving patient outcomes.
Clinical Evaluation
A thorough clinical evaluation is essential for diagnosing joint diseases. It starts with a detailed medical history to identify symptoms and previous injuries. A physical examination then assesses joint mobility, pain, swelling, and signs of inflammation or damage.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are vital in diagnosing joint diseases. Blood tests can detect inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). These markers are often high in inflammatory arthritis. Tests for rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibodies help diagnose rheumatoid arthritis.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques offer valuable insights into joint health and disease progression. Various modalities are used, each with its own advantages.
X-rays and CT Scans
X-rays are commonly used to assess joint damage and bone spurs. CT scans provide more detailed images, useful for complex joint structures and bone erosions.
MRI and Ultrasound
MRI is highly sensitive for detecting soft tissue abnormalities and early joint inflammation. Ultrasound is useful for assessing synovial inflammation and guiding injections or aspirations.
Synovial Fluid Analysis
Synovial fluid analysis involves aspirating fluid from the joint space. It can diagnose conditions like gout or septic arthritis. This procedure identifies crystal deposition, infection, or other joint abnormalities.
By combining these diagnostic approaches, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose and manage joint diseases. This improves patient outcomes and quality of life.
Conventional Medical Treatments
Conventional medical treatments are vital for easing symptoms and slowing disease progression in joint diseases. These methods aim to enhance the quality of life for those affected. They include a variety of approaches tailored to individual needs.
Pharmacological Interventions
Pharmacological interventions are fundamental in managing joint diseases. They involve different types of medications, each chosen based on the patient’s specific requirements.
Pain Management Medications
Pain management is a key component in treating joint diseases. To alleviate pain and inflammation, medications like NSAIDs and analgesics are frequently prescribed.
- NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen)
- Analgesics (e.g., acetaminophen)
- Corticosteroids for short-term relief
Disease-Modifying Drugs
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are used to slow disease progression in inflammatory arthritis. Methotrexate and sulfasalazine are examples of these drugs.
Physical and Occupational Therapy
Physical and occupational therapy are essential for maintaining joint mobility and function. These therapies enable patients to perform daily tasks more efficiently.
Physical therapy includes exercises and interventions to enhance joint mobility and strength. Occupational therapy, on the other hand, focuses on adapting daily activities to the patient’s capabilities.
Assistive Devices
Assistive devices are critical for aiding patients in their daily activities. These devices help reduce joint strain and improve mobility.
- Canes and walkers for support
- Orthotic devices for joint stabilization
- Adaptive tools for daily living activities
Surgical Options for Joint Diseases
For those with severe joint diseases, surgery can offer significant relief and enhance quality of life. When non-surgical treatments fail, surgery becomes a viable option.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure for diagnosing and treating joint conditions. It involves using a small camera and instruments through tiny incisions. This allows for the joint’s examination and treatment with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.
Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement surgery replaces damaged or arthritic joints with prosthetic components. This procedure is often performed on hips, knees, and shoulders. It can greatly improve joint function and reduce pain.
Synovectomy
A synovectomy removes inflamed synovial tissue, common in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. This procedure reduces inflammation, alleviating pain and improving joint function.
Osteotomy
Osteotomy involves cutting and realigning bones to redistribute weight-bearing stress or correct deformities. It’s beneficial for patients with malaligned joints or uneven wear.
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
Post-surgical rehabilitation is key to recovery after joint surgery. A structured rehabilitation program helps patients regain strength, mobility, and function. It ensures the best possible outcomes.
Emerging Therapies and Research
Emerging therapies are transforming the way we manage joint diseases, leading to better outcomes for patients. Recent breakthroughs in medical research have opened doors to new treatments. These address the underlying causes of joint diseases more directly.
Biologics and Targeted Therapies
Biologics and targeted therapies are changing the treatment scene for inflammatory arthritis. They target specific molecules in the inflammatory process. This offers relief to those who haven’t seen results from traditional treatments.
Stem Cell Treatments
Stem cell treatments are being studied for their ability to repair damaged joints. Researchers aim to use stem cells’ regenerative powers. They hope to restore joint function and lessen pain.
Gene Therapy Approaches
Gene therapy is also being explored. It involves modifying or replacing genes linked to joint disease. This approach could potentially stop disease progression and even reverse damage.
Promising Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials are underway, testing new treatments. These include novel biologics, stem cell therapies, and gene editing. These trials are essential for moving these emerging therapies from the lab to patients.
The outlook for managing joint diseases is bright with these new therapies and ongoing research. As we learn more about joint diseases, our treatment options improve. This means we can tackle these conditions more effectively.
Preventing Joint Diseases
Preventing joint diseases requires a proactive approach, focusing on individual and environmental factors. By taking preventive steps, individuals can lower their risk of joint-related conditions.
Early Intervention Strategies
Early intervention is key in stopping joint diseases from getting worse. Regular health check-ups help monitor joint health and address issues quickly. Spotting risk factors early allows for timely action, including lifestyle changes and medical treatments if needed.
Joint-Protective Techniques
Joint-protective techniques are essential for reducing joint stress. Using assistive devices, modifying daily activities, and maintaining proper posture are all important. 
- Utilizing ergonomic furniture and tools
- Avoiding repetitive strain injuries
- Engaging in exercises that strengthen the muscles around the joints
Maintaining Healthy Body Weight
Keeping a healthy body weight is critical for avoiding degenerative joint conditions. Excess weight increases stress on joints like knees and hips, speeding up wear and tear. A balanced diet and regular exercise help maintain a healthy weight.
Workplace Ergonomics
Workplace ergonomics are vital in preventing joint injuries at work. Setting up workstations to promote good posture and reduce strain is essential. This includes adjusting chair heights, monitor angles, and keyboard positions for comfort.
Nutritional Approaches to Managing Joint Diseases
Nutrition is key in easing joint disease symptoms. A well-rounded nutritional plan can manage the condition and enhance life quality for those affected.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet Principles
An anti-inflammatory diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can reduce inflammation. Foods high in antioxidants, like berries and leafy greens, are very beneficial.
Key Nutrients for Joint Health
Some nutrients are vital for joint health. Glucosamine and chondroitin support cartilage, while omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation.
Dietary Supplements
Alongside a balanced diet, certain supplements can offer extra benefits for joint health.
Glucosamine and Chondroitin
Glucosamine and chondroitin supplements are often used to support joint health and lessen osteoarthritis symptoms.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil supplements, have anti-inflammatory effects. They can help reduce joint pain and inflammation.
Antioxidants
Antioxidant supplements, such as vitamin C and E, protect joints from oxidative stress and damage.
By adopting these nutritional strategies, individuals with joint diseases can potentially lessen their symptoms. This can also improve their overall joint health.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Complementary and alternative therapies provide more ways to manage joint diseases, alongside traditional treatments. They aim to offer relief and enhance quality of life. These methods can be used in conjunction with conventional medical approaches.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific body points to ease pain and aid healing. This ancient method has proven effective in reducing pain and boosting function in those with joint diseases.
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy helps reduce muscle tension, improves joint mobility, and promotes relaxation. Regular sessions can greatly benefit individuals with joint diseases, improving their overall well-being.
Mind-Body Approaches
Mind-body approaches, like meditation and yoga, focus on relaxation and stress reduction. These practices can help manage symptoms and enhance mental health in those with joint diseases.
Herbal Remedies
Herbal remedies, such as turmeric and ginger, have anti-inflammatory properties. They may help alleviate symptoms of joint diseases. For those considering surgery, visiting a reputable healthcare provider like Acibadem International can provide insights into knee surgery and other treatment options.
Living with Chronic Joint Diseases
Dealing with chronic joint diseases goes beyond just medical treatment. It demands a holistic approach that touches on various aspects of daily living. Effective management can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain management is a key aspect of living with chronic joint diseases. It involves medication, physical therapy, and alternative therapies like acupuncture. A healthcare provider can help tailor the most effective pain management plan.
Adaptive Techniques
Adaptive techniques and assistive devices are essential for daily activities. Tools like canes, walkers, or ergonomic furniture can lessen joint strain. Occupational therapy offers personalized advice for adapting daily routines.
Support Systems
A strong support system is critical for those with chronic joint diseases. Family, friends, and support groups provide emotional support and practical help. Connecting with others who face similar challenges can be incredibly beneficial.
Mental Health Considerations
Mental health is a significant factor in managing chronic joint diseases. Anxiety and depression are common among those with chronic conditions. Seeking professional help and practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as mindfulness or meditation, can be beneficial.
By integrating these strategies into daily life, individuals with chronic joint diseases can better manage their condition. This can significantly improve their overall well-being.
Advancing Our Understanding of Joint Health
Ongoing research is essential for creating effective treatments for joint diseases. It’s vital to explore the causes and effects of these conditions to enhance patient outcomes. New technologies, like biomarkers and advanced imaging, are improving diagnosis and treatment.
Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patients is driving progress in joint health. By working together, we can speed up the development of new therapies. This collaboration is leading to better management strategies and improved quality of life for those with joint disorders.
The future of joint health research is promising, with breakthroughs in regenerative medicine and personalized treatments on the horizon. As our knowledge of joint health grows, we can expect more effective and targeted interventions.
FAQ
Q: What are the most common types of joint diseases?
A: Common joint diseases include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis. Gout and ankylosing spondylitis are also prevalent.
Q: What are the symptoms of joint diseases?
A: Symptoms include pain, swelling, and stiffness. Limited mobility and inflammation are also common. Fever and fatigue can occur as well.
Q: How are joint diseases diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, lab tests, and imaging. X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound are used. Synovial fluid analysis is also part of the process.
Q: What are the treatment options for joint diseases?
A: Treatments include pharmacological interventions and physical therapy. Assistive devices and surgery, like arthroscopy, are also options. Joint replacement and synovectomy are considered when necessary.
Q: Can joint diseases be prevented?
A: Prevention is possible for some conditions. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding repetitive strain injuries can help. These actions reduce the risk of certain joint diseases.
Q: What are some emerging therapies for joint diseases?
A: New therapies include biologics and targeted therapies. Stem cell treatments and gene therapy are being explored. They aim to repair damaged joints.
Q: How can nutrition impact joint health?
A: An anti-inflammatory diet helps alleviate symptoms. It includes fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids. Glucosamine and chondroitin support joint health as well.
Q: What are some complementary and alternative therapies for joint diseases?
A: Complementary therapies include acupuncture and massage therapy. Mind-body approaches and herbal remedies are also used. They complement conventional treatments.
Q: How can individuals live with chronic joint diseases?
A: Living with chronic joint diseases requires adapting. Pain management and adaptive techniques are essential. Support systems and mental health considerations are also important.