Mediastinoscopy: What is Mediastinoscopy?
Mediastinoscopy is a diagnostic surgical procedure that allows doctors to examine the mediastinum. This area in the chest contains the heart, trachea, esophagus, and lymph nodes. It’s essential for diagnosing and staging conditions like lung cancer and lymphoma. Physicians use a mediastinoscope through a small chest incision. This allows them to visually inspect the mediastinum and collect tissue samples. The procedure is minimally invasive, providing vital information for treatment decisions. It’s a key tool in patient care. Mediastinoscopy is a surgical method used to diagnose and stage medical conditions. It involves examining the mediastinum, a chest area with the heart, trachea, esophagus, and lymph nodes. This procedure is vital for understanding the extent of diseases like lung cancer and lymphoma.
Definition and Purpose
Mediastinoscopy is a diagnostic surgery that looks into the mediastinum and takes tissue samples. Its main goal is to accurately diagnose and stage conditions such as lung cancer and lymphoma. This helps in planning the right treatment.
The benefits of mediastinoscopy are numerous:
- Accurate diagnosis of mediastinal conditions
- Staging of cancers for appropriate treatment planning
- Minimally invasive approach reducing recovery time
Types of Mediastinoscopy Procedures
There are various approaches to mediastinoscopy:
- Standard mediastinoscopy, which involves making an incision in the neck to access the mediastinum.
- Video-assisted mediastinoscopy, which uses a video camera to enhance visualization during the procedure.
- Extended mediastinoscopy, an advanced technique that allows for broader access to the mediastinum.
Mediastinoscopy has evolved, incorporating different techniques. Each has its own benefits and specific uses. The choice of procedure depends on the patient’s condition and the diagnostic goals.
The Anatomy of the Mediastinum
The mediastinum’s anatomy is complex and vital for both respiratory and cardiac health. It is the central part of the chest cavity. It contains essential structures critical for overall health.
Structures Within the Mediastinum
The mediastinum is home to critical organs and tissues. These include the heart, trachea, esophagus, thymus gland, and various lymph nodes. They are essential for blood circulation, breathing, and immune response.
The heart and major blood vessels are located within the mediastinum. They play a key role in cardiovascular health. The trachea and esophagus are also vital, facilitating breathing and digestion, respectively.
Importance in Respiratory and Cardiac Health
The mediastinum’s structures are integral to both respiratory and cardiac functions. Diseases affecting the mediastinum, such as tumors or infections, can have significant implications for these vital systems.
Understanding the mediastinum’s anatomy is critical for diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the heart, lungs, and surrounding tissues. Procedures like mediastinoscopy rely on this knowledge to explore and sample tissues within the mediastinum.
Medical Conditions Diagnosed Through Mediastinoscopy
Mediastinoscopy is a key diagnostic tool for identifying various medical conditions affecting the mediastinum. It allows for the direct examination of the mediastinal lymph nodes and other structures within the chest cavity.
The information obtained through mediastinoscopy is vital for diagnosing and staging several serious health conditions. It provides healthcare professionals with the necessary details to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Lung Cancer Staging
Lung cancer staging is a primary use of mediastinoscopy. By examining the mediastinal lymph nodes, doctors can determine if lung cancer has spread beyond the lungs. This is critical for staging the disease accurately.
- Accurate staging helps in choosing the most effective treatment strategy.
- Mediastinoscopy can identify cancer spread to lymph nodes that may not be visible on imaging tests.
- This information is critical for determining the prognosis and possible surgical options.
Lymphoma Detection
Mediastinoscopy is also used in the diagnosis and staging of lymphoma, including Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The procedure allows for the sampling of lymph nodes in the mediastinum, which can be affected by lymphoma.
The tissue samples obtained through mediastinoscopy help confirm the diagnosis and identify the specific type of lymphoma. This guides treatment decisions.
Other Conditions
Apart from lung cancer and lymphoma, mediastinoscopy can aid in diagnosing other conditions such as sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, and other granulomatous diseases.
These conditions often present with enlarged lymph nodes or masses in the mediastinum. Mediastinoscopy provides a direct method for obtaining tissue for pathological examination.
In summary, mediastinoscopy is a valuable diagnostic tool for a range of conditions affecting the mediastinum. It provides critical information for diagnosis, staging, and treatment planning.
When is a Mediastinoscopy Necessary?
Understanding when mediastinoscopy is necessary requires insight into its diagnostic capabilities. This procedure offers direct access to the mediastinum, allowing for tissue and lymph node sampling. It’s invaluable when other diagnostic methods fall short or when a clear diagnosis is needed for treatment planning.
Common Indications
Mediastinoscopy is often used for diagnosing and staging lung cancer, lymphoma, and other mediastinal conditions. It’s employed when imaging studies reveal abnormalities that need tissue confirmation. Common reasons include:
- Abnormal lymph node enlargement
- Suspicious masses in the mediastinum
- Need for lung cancer staging
- Diagnosis of lymphoma or other malignancies
Alternative Diagnostic Methods
Though mediastinoscopy is a powerful tool, other methods like CT scans, PET scans, and needle biopsies are also available. These alternatives are preferred in some cases for their less invasive nature. Yet, mediastinoscopy remains the top choice for obtaining mediastinal tissue samples, essential for precise staging.
The Mediastinoscopy Procedure Explained
Mediastinoscopy is a surgical method for diagnosing conditions in the mediastinum. It enables doctors to visually inspect the mediastinum and obtain tissue samples for analysis.
Anesthesia Administration
Before starting the mediastinoscopy, patients receive general anesthesia. This ensures they are comfortable and pain-free during the procedure. An anesthesiologist, who closely monitors vital signs, administers the anesthesia.
- The patient is given general anesthesia to induce unconsciousness.
- An anesthesiologist is present to monitor the patient’s vital signs.
- The anesthesia ensures the patient feels no pain during the procedure.
Surgical Technique
The mediastinoscopy procedure demands precision and skill. It involves a small chest incision, typically in the suprasternal notch, for inserting a mediastinoscope.
The mediastinoscope, equipped with a camera and light, allows the surgeon to see the mediastinum on a monitor. The surgeon then explores the mediastinum, identifying lymph nodes or other structures of interest.
- A small incision is made in the suprasternal notch.
- The mediastinoscope is inserted through the incision.
- The surgeon examines the mediastinum using the mediastinoscope’s camera.
Tissue Sampling Process
During the mediastinoscopy, the surgeon takes tissue samples from lymph nodes or other areas in the mediastinum. These samples are then analyzed in a pathology laboratory.
- Tissue samples are collected using specialized instruments.
- The samples are sent to a pathology lab for examination.
- The pathology report aids in diagnosing conditions like lung cancer or lymphoma.
Preparing for Your Mediastinoscopy
To ensure a smooth and successful mediastinoscopy, patients must follow specific pre-procedure guidelines. Proper preparation not only helps in reducing risks but also contributes to a more efficient recovery process. This section outlines the necessary steps and guidelines to follow before undergoing a mediastinoscopy.
Medical Evaluations Before the Procedure
Before a mediastinoscopy, patients undergo a series of medical evaluations. These evaluations assess their overall health and identify any risks. A thorough medical history review, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests are part of this process. Blood work and imaging studies are common, along with assessments of cardiac and respiratory function.
Dietary and Medication Guidelines
Patients are required to follow specific dietary and medication guidelines before a mediastinoscopy. This includes fasting for a certain period and adjusting or temporarily discontinuing certain medications. It’s essential to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions to minimize risks.
What to Bring to the Hospital
On the day of the mediastinoscopy, patients should bring essential items to the hospital. This includes identification, insurance information, and a list of their medications. Comfortable clothing and personal items needed during recovery should also be brought. Having a friend or family member accompany the patient can provide emotional support and assistance.
Healthcare Professionals Involved in Mediastinoscopy
The success of a mediastinoscopy hinges on the skill of thoracic surgeons and their surgical team. This complex procedure demands precise coordination among healthcare professionals. It ensures accurate diagnosis and effective patient care.
Thoracic Surgeons
Thoracic surgeons lead in performing mediastinoscopy. They specialize in surgeries of the chest cavity, including the lungs and esophagus. Their expertise is vital for diagnosing and staging conditions like lung cancer and lymphoma.
The Surgical Team
The surgical team backing thoracic surgeons includes anesthesiologists, nurses, and surgical technicians. Anesthesiologists provide anesthesia for patient comfort during the procedure. Nurses and technicians prepare the operating room, maintain sterility, and care for patients before and after surgery.
Potential Risks and Complications
The risks and complications of mediastinoscopy, though rare, are critical for both patients and healthcare providers. The procedure is generally safe. Yet, knowing these possible issues aids in making informed decisions.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects of mediastinoscopy include temporary discomfort or pain at the incision site. Mild swelling or bruising may also occur. If a breathing tube was used, some patients might experience a sore throat. These side effects are usually short-lived and can be managed with proper post-operative care.
Serious Complications
Serious complications, though rare, can happen. These may include infection, bleeding, or injury to nearby structures like nerves or blood vessels. In severe cases, complications might require additional medical intervention or extended hospital stays.
Risk Factors for Complications
Certain factors can raise the risk of complications during or after mediastinoscopy. These include pre-existing medical conditions, such as heart disease or diabetes. Previous surgeries or radiation therapy in the chest area also increase risk. Understanding these risk factors is key to managing expectations and minimizing complications.
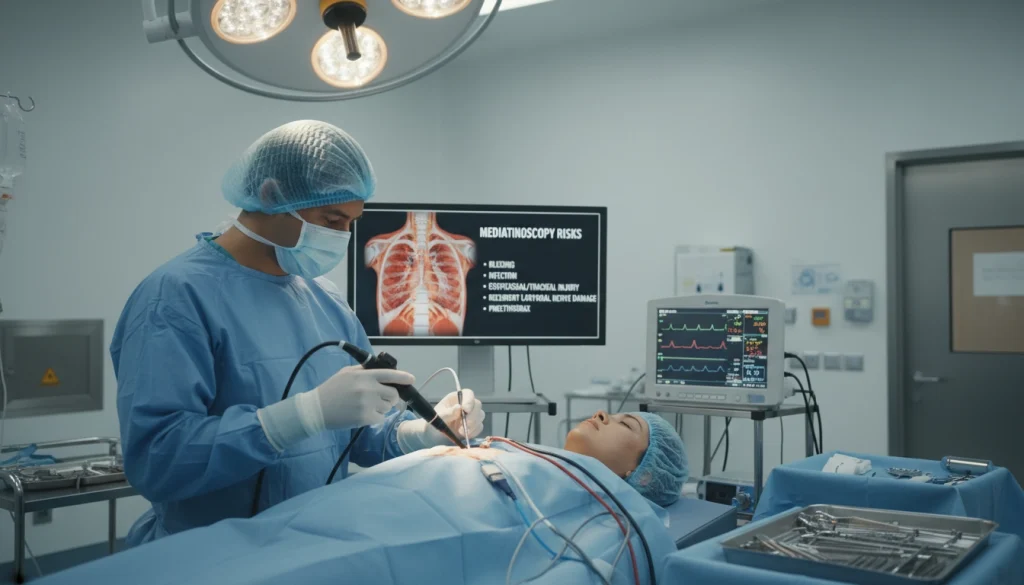
Recovery After Mediastinoscopy
Knowing what to expect during recovery can ease concerns for those who’ve had a mediastinoscopy. The recovery journey includes several important aspects. Being aware of these can help ensure a smooth and safe healing process.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Patients are taken to the recovery room post-procedure. Here, they are closely monitored for any immediate issues. The medical team checks vital signs and manages pain or discomfort.
- Patients are typically monitored for a few hours before being discharged or taken to their hospital room.
- Pain management is a priority, with medication provided as needed.
- Patients are also monitored for any signs of complications, such as difficulty breathing or severe pain.
Hospital Discharge Guidelines
Before discharge, patients receive detailed care instructions for at-home recovery. This includes guidance on wound care, medication, and follow-up appointments.
- Patients are advised on how to keep the surgical site clean and dry.
- Guidance is provided on managing pain and other symptoms.
- Follow-up appointments are scheduled to check on the patient’s recovery progress.
Activity Restrictions
Patients are advised on activity restrictions to aid in healing. This includes avoiding heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities for a specified period.
By adhering to these guidelines, patients can reduce the risk of complications. This ensures a successful recovery.
Understanding Your Mediastinoscopy Results
Grasping the outcomes of a mediastinoscopy is essential for patients. It helps them understand their diagnosis and the treatment options available. After the procedure, tissue samples are sent to a pathology lab for examination.
Timeframe for Results
The time it takes to get mediastinoscopy results varies from a few days to a week. This timeframe depends on the analysis complexity and the lab’s workload.
Interpreting Pathology Reports
Pathology reports outline the findings from tissue samples. These reports are key for diagnosing conditions like lung cancer or lymphoma. A healthcare provider will explain these results, discussing their implications for your health.
Next Steps Based on Findings
After receiving the mediastinoscopy results, your healthcare team will discuss the next steps. This could include further diagnostic tests, treatment options, or starting a treatment plan already decided.
Follow-Up Care After Mediastinoscopy
Proper follow-up care is vital for patients post-mediastinoscopy. It ensures a smooth recovery and addresses any complications promptly. This care is essential for the patient’s well-being.
Post-Procedure Appointments
Patients must attend follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider post-mediastinoscopy. These visits monitor the patient’s recovery and check the biopsy site for complications. It’s a critical step in the healing process.
- Follow-up appointments are usually scheduled within a week or two after the procedure.
- During these visits, the healthcare provider will assess the patient’s overall condition and check for any signs of complications.
- Patients should use these opportunities to ask questions and report any concerns they may have.
When to Contact Your Doctor
Knowing when to seek medical attention after a mediastinoscopy is key. While some discomfort is normal, certain symptoms require immediate attention.
- Severe pain or difficulty breathing.
- Fever or signs of infection at the biopsy site.
- Any unusual or concerning symptoms.
Patients should not hesitate to contact their doctor if they experience any of these symptoms. Prompt attention can prevent minor issues from becoming more serious.
Mediastinoscopy vs. Other Diagnostic Procedures
Several diagnostic methods are available for examining the mediastinum, including mediastinoscopy, CT scans, PET scans, and needle biopsies. Each has its own advantages and limitations.
Comparison with CT and PET Scans
CT and PET scans offer valuable insights into the mediastinum. Yet, they might not always pinpoint the exact issue.
- CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the mediastinum.
- PET scans highlight areas of high metabolic activity, which could signal cancer or infection.
- Though useful for cancer staging and detecting abnormalities, these scans lack the ability to provide tissue samples for pathological examination.
Comparison with Needle Biopsies
Needle biopsies collect tissue samples from the mediastinum using a needle. They are less invasive than mediastinoscopy but might not always yield enough tissue for a definitive diagnosis.
- Needle biopsies are quicker and less invasive than mediastinoscopy.
- Yet, they often lack the tissue needed for thorough pathological analysis.
When Mediastinoscopy is Preferred
Mediastinoscopy is favored when a detailed mediastinum examination is needed or when other methods fail to provide clear results.
- Mediastinoscopy allows for direct visualization and sampling of mediastinal tissues.
- It’s highly beneficial for lung cancer staging and diagnosing lymphoma.
Cost and Insurance Coverage for Mediastinoscopy
Understanding the costs and insurance coverage for a mediastinoscopy is key to financial planning. Patients must grasp the expenses involved in this diagnostic procedure. This knowledge helps them make informed decisions about their care.
Average Procedure Costs
The cost of a mediastinoscopy varies due to several factors. These include the location, surgeon fees, and additional tests needed. On average, the total cost in the United States can range from $8,000 to $15,000 or more. This includes the surgeon’s fee, hospital charges, anesthesia, and pathology services for tissue analysis.
Insurance Considerations
Insurance coverage for mediastinoscopy depends on the patient’s plan. Most plans cover necessary diagnostic procedures like mediastinoscopy. Yet, patients should confirm their coverage and any out-of-pocket costs, like deductibles or copays. It’s also vital to ensure the providers and facilities are in-network to reduce costs.
Living with a Mediastinoscopy Scar
Understanding how to manage and care for the scar after a mediastinoscopy is key for patients’ recovery. The scar results from the surgical incision made during the procedure. Proper care can minimize its appearance and ensure a smoother healing process.
Scar Healing Process
The healing process of a mediastinoscopy scar typically begins immediately after the surgery. Initially, the scar may appear red, swollen, and tender. Over time, it will start to fade and become less noticeable. Keeping the scar moisturized and protected from the sun can aid in the healing process.
Scar Management Techniques
Effective scar management involves a combination of proper wound care, scar massage, and protection from the sun. Silicone gel or sheeting can also be used to help flatten and soften the scar tissue. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s advice on the best scar management techniques.
Advanced Techniques in Modern Mediastinoscopy
Advances in medical technology have significantly improved mediastinoscopy procedures. These advancements have boosted both the accuracy and safety of the diagnostic process.
Video-Assisted Approaches
Video-assisted mediastinoscopy marks a major leap forward in the field. It employs a video camera to offer a clear view of the mediastinum. This allows for more precise tissue sampling.
The introduction of video assistance has enhanced the visibility of anatomical structures. This has lowered the risk of complications during the procedure.
Minimally Invasive Innovations
Minimally invasive innovations in mediastinoscopy have minimized the need for large incisions. This results in less trauma to the patient. Innovations include the use of smaller instruments and advanced imaging technologies.
These advancements have led to quicker recovery times and less post-operative pain for patients undergoing mediastinoscopy.
Key Takeaways About Mediastinoscopy
Mediastinoscopy is a key diagnostic tool that offers insights into the mediastinum, a vital part of the chest cavity. It’s essential for diagnosing and staging conditions like lung cancer and lymphoma.
A summary of mediastinoscopy emphasizes its importance in patient care. It enables healthcare professionals to collect tissue samples for pathological examination. This guides treatment decisions and enhances patient outcomes.
The benefits of mediastinoscopy include its minimally invasive nature and low risk of complications. It also provides accurate diagnoses. Understanding the procedure, its indications, and outcomes is vital for both patients and healthcare providers.
By summarizing the main points about mediastinoscopy, patients gain a better understanding of what to expect. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions about their health.
FAQ
Q: What is mediastinoscopy?
A: Mediastinoscopy is a surgical method that lets doctors examine the mediastinum. This area in the chest houses the heart, trachea, esophagus, and lymph nodes. It involves inserting a scope through a neck incision.
Q: Why is mediastinoscopy performed?
A: It’s used to diagnose and stage lung cancer, lymphoma, and other mediastinal conditions. It also helps assess cancer spread to lymph nodes.
Q: What are the risks associated with mediastinoscopy?
A: Risks include bleeding, infection, damage to nearby structures, and adverse anesthesia reactions.
Q: How long does it take to recover from mediastinoscopy?
A: Recovery spans a few days to a week. Patients may feel discomfort, fatigue, and swelling at the incision site.
Q: Will I have a scar after mediastinoscopy?
A: Yes, a small scar will form at the incision site. It heals over time. Techniques for managing scars can reduce its visibility.
Q: Can mediastinoscopy be used instead of other diagnostic tests?
A: It’s often used alongside CT and PET scans for a more accurate diagnosis. In some cases, it’s preferred over other methods.
Q: How much does mediastinoscopy cost?
A: Costs vary by location, insurance, and procedure complexity. On average, it can range from several thousand dollars.
Q: Is mediastinoscopy covered by insurance?
A: Many insurance plans cover it when deemed medically necessary. Patients should confirm coverage and any out-of-pocket costs with their provider.
Q: What kind of anesthesia is used for mediastinoscopy?
A: General anesthesia is used to keep the patient comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
Q: How long does a mediastinoscopy procedure take?
A: It usually takes 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the case’s complexity.