Mitral Valve Insufficiency: What is Mitral Valve Insufficiency?
Mitral Valve Insufficiency is a heart disorder where the mitral valve fails to close correctly. It impacts millions globally, posing a significant health risk. Without proper treatment, this condition can lead to severe complications. It’s essential to grasp its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
This article delves into Mitral Valve Insufficiency, focusing on diagnosis, treatment, and management. Our goal is to educate readers about this critical heart condition. Mitral Valve Insufficiency, or mitral regurgitation, happens when the mitral valve doesn’t close right. This causes blood to leak back into the left atrium from the left ventricle during systole. It’s vital to understand this condition to appreciate its impact on heart health.
Definition and Basic Concepts
Mitral Valve Insufficiency is marked by the mitral valve leaflets not closing fully, leading to blood leakage. The mitral valve is key, separating the left atrium from the left ventricle. It ensures blood flows correctly through the heart. Knowing the anatomy and function of the mitral valve, along with the hemodynamic changes caused by insufficiency, is essential.
- The mitral valve has two leaflets: the anterior and posterior.
- Its proper closure is critical to prevent backflow.
- Various factors, like degenerative changes and rheumatic heart disease, can cause it.
Prevalence and Significance
Mitral Valve Insufficiency is a major heart disease, affecting many people. It becomes more common with age, posing a significant risk to the elderly. Research indicates that it impacts a large number of individuals globally, with varying severity levels.
- It’s one of the most prevalent valvular heart diseases.
- Untreated, it can lead to serious health issues.
- It significantly affects quality of life and healthcare systems.
The importance of Mitral Valve Insufficiency cannot be overstated. It can lead to heart failure, arrhythmias, and other serious complications. Early detection and treatment are critical for better outcomes in those affected.
Anatomy and Function of the Mitral Valve
To grasp the importance of mitral valve insufficiency, we must first understand its normal anatomy and function. The mitral valve is a complex structure. It plays a vital role in cardiac circulation.
Normal Structure and Components
The mitral valve has several key components. These include the valve leaflets, annulus, chordae tendineae, and papillary muscles. Together, they ensure the valve functions properly.
- The valve leaflets are responsible for opening and closing the valve.
- The annulus provides a ring-like structure that supports the leaflets.
- The chordae tendineae and papillary muscles help to control the leaflets’ movement.
Role in Cardiac Circulation
The mitral valve is essential for efficient cardiac circulation. It allows blood to flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle during diastole. It prevents backflow during systole.
Proper functioning of the mitral valve ensures the heart pumps blood effectively. Any dysfunction can lead to significant cardiac complications.
Types of Mitral Valve Insufficiency
It’s vital to grasp the different types of Mitral Valve Insufficiency to choose the right treatment. This condition, known as Mitral Regurgitation, is classified based on its cause and how long it lasts.
Primary (Degenerative) Mitral Regurgitation
Primary Mitral Regurgitation stems from wear and tear on the mitral valve, affecting its parts like the leaflets and chordae tendineae. It’s often caused by mitral valve prolapse or chordal rupture. This degeneration can cause significant leakage, requiring surgery.
The defining features of primary mitral regurgitation include:
- Degenerative changes in the valve structure
- Presence of mitral valve prolapse or leaflet flail
- Potential for chordal rupture
Secondary (Functional) Mitral Regurgitation
Secondary Mitral Regurgitation is triggered by issues affecting the left ventricle, like coronary artery disease. It results in valve dysfunction without any initial valve damage. This condition is linked to left ventricular remodeling and enlargement.
Acute vs. Chronic Insufficiency
Mitral Valve Insufficiency can be acute or chronic. Acute cases happen suddenly, often due to trauma or infections, leading to quick worsening. Chronic cases develop slowly, allowing the body to adapt.
The main distinctions between acute and chronic insufficiency are:
- Onset: Sudden in acute, gradual in chronic
- Clinical presentation: Severe symptoms in acute, potentially mild in chronic
- Compensatory mechanisms: Absent or minimal in acute, present in chronic
Common Causes of Mitral Valve Insufficiency
The etiology of Mitral Valve Insufficiency is complex, involving various cardiac and systemic conditions. Grasping these causes is vital for diagnosing and managing the condition effectively.
Degenerative Disorders
Degenerative disorders significantly contribute to Mitral Valve Insufficiency. Issues like mitral valve prolapse and calcification of the mitral annulus can impair valve function. These changes often stem from aging, but hypertension and atherosclerosis can accelerate them.
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Rheumatic heart disease is a major cause of Mitral Valve Insufficiency, more so in areas where rheumatic fever is common. Rheumatic fever’s inflammation can scar and deform the mitral valve, causing insufficiency.
Infective Endocarditis
Infective endocarditis, an infection of the heart valves, can also lead to Mitral Valve Insufficiency. This infection damages the valve leaflets and surrounding tissue, impairing valve function.
Other Causative Factors
Other factors contributing to Mitral Valve Insufficiency include traumatic chest injuries, cardiomyopathy, and certain connective tissue disorders. These conditions can alter the mitral valve’s structure and function, causing insufficiency.
In summary, Mitral Valve Insufficiency arises from diverse causes, including degenerative disorders, rheumatic heart disease, infective endocarditis, and other factors. Recognizing these causes is essential for effective management and treatment.
Risk Factors for Developing Mitral Valve Insufficiency
The risk of Mitral Valve Insufficiency is shaped by age, genetics, and lifestyle. Knowing these factors helps identify those at higher risk. It also guides preventive actions.
Age-Related Factors
Age is a key risk factor for Mitral Valve Insufficiency. Older adults face a higher risk due to heart valve wear and tear. Over time, the mitral valve can thicken or calcify, causing insufficiency.
Genetic Predispositions
Genetics also significantly influence Mitral Valve Insufficiency. Those with a family history of heart valve issues or conditions like Marfan syndrome are at greater risk. Genetic factors can alter the mitral valve’s structure and function, making it more prone to insufficiency.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle and environmental factors, such as hypertension, obesity, and smoking, also play a role. These can strain the heart and impact the mitral valve’s function, raising the risk of insufficiency. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce these risks.
Recognizing Symptoms of Mitral Valve Insufficiency
Identifying the symptoms of Mitral Valve Insufficiency is key to effective management and treatment. This condition, also known as Mitral Regurgitation, happens when the mitral valve doesn’t close right. This allows blood to flow backward in the heart. It’s important to recognize these symptoms early to ensure timely treatment.
Early Warning Signs
Early signs of Mitral Valve Insufficiency include fatigue, shortness of breath, and palpitations. These symptoms happen because the heart has to work harder due to inefficient blood flow.
- Fatigue due to reduced cardiac output
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea) during normal activities
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeats
Progressive Symptoms
As Mitral Valve Insufficiency worsens, symptoms intensify. People may notice swelling in their legs and feet, coughing, and a drop in exercise ability. These signs indicate worsening heart function and the need for medical check-ups.
- Swelling (edema) in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Coughing, potentially producing frothy sputum
- Reduced ability to perform physical activities
Severe Manifestations
In severe cases, Mitral Valve Insufficiency can cause acute decompensated heart failure. This is marked by severe shortness of breath, difficulty breathing when lying down, and waking up with shortness of breath. These symptoms demand immediate medical care.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seeking medical help is essential if symptoms persist or get worse. Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve outcomes for those with Mitral Valve Insufficiency. If you’re experiencing severe symptoms or if they’re impacting your daily life, see a healthcare professional right away.
Diagnostic Approaches and Testing
Diagnosing Mitral Valve Insufficiency involves a combination of physical examination and advanced imaging. Accurate diagnosis is key to understanding the condition’s severity and choosing the right treatment.
Physical Examination Findings
The first step in diagnosing Mitral Valve Insufficiency is a thorough physical examination. Healthcare providers use a stethoscope to listen for heart murmurs, which can signal abnormal blood flow. A holosystolic murmur is often a sign of this condition.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is essential for diagnosing and assessing Mitral Valve Insufficiency. Various methods are used to see the heart’s structure and function.
Echocardiography
Echocardiography is a primary tool for diagnosing Mitral Valve Insufficiency. It gives detailed images of the mitral valve, allowing for its structure and function to be assessed. Doppler echocardiography can measure the severity of mitral regurgitation.
Advanced Imaging Methods
Advanced imaging, like cardiac MRI or CT scans, may be used in some cases. These methods provide more information on the heart’s anatomy and the extent of valve dysfunction.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests, including blood tests, are used to assess heart health and identify underlying causes of Mitral Valve Insufficiency. These tests help evaluate conditions that may lead to mitral regurgitation.
Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is an invasive procedure used in some cases to assess Mitral Valve Insufficiency. It involves inserting a catheter into the heart to measure pressures and see the coronary arteries. This procedure offers valuable information for treatment decisions.
By combining findings from physical examination, imaging, laboratory tests, and cardiac catheterization, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose Mitral Valve Insufficiency. This allows for the development of an effective treatment plan.
Grading and Classification Systems
Grading and classification systems are essential in managing Mitral Valve Insufficiency. They offer a standardized method to assess its severity. This helps clinicians understand the extent of the condition and make informed treatment decisions.
Severity Scales
Severity scales quantify the degree of Mitral Valve Insufficiency. Echocardiography is commonly used to measure regurgitant volume, fraction, and effective orifice area. These metrics help classify the condition as mild, moderate, or severe. This classification is critical for determining the best management strategy.
Functional Classification
Functional classification systems, like the New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification, evaluate patients with Mitral Valve Insufficiency. It categorizes patients based on symptoms and exercise tolerance, from Class I (no symptoms) to Class IV (symptoms at rest). The NYHA classification is vital for understanding a patient’s quality of life and tailoring treatment plans.
Medical Management of Mitral Valve Insufficiency
Managing Mitral Valve Insufficiency effectively involves a detailed plan. This includes medication, regular monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments. The goal is to ease symptoms, slow disease progression, and enhance the patient’s quality of life.
Pharmacological Treatments
Pharmacological treatments are key in managing Mitral Valve Insufficiency. ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and diuretics are commonly prescribed. ACE inhibitors widen blood vessels, reducing heart workload. Beta-blockers slow the heart rate, improving its efficiency. Diuretics reduce fluid buildup, easing symptoms like shortness of breath.
Monitoring and Follow-up Protocols
Regular monitoring is vital for patients with Mitral Valve Insufficiency. Echocardiograms are used to assess condition severity and track changes. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are also essential. They allow for treatment adjustments and address any concerns or symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes are critical in managing Mitral Valve Insufficiency. Patients are advised to maintain a healthy weight, follow a low-sodium diet, and engage in regular physical activity. Quitting smoking is also recommended, as it can worsen heart conditions. These lifestyle adjustments help reduce symptoms and improve overall health.
Surgical and Interventional Treatments
Mitral Valve Insufficiency can be effectively managed with surgical and interventional treatments. These treatments aim to restore the normal functioning of the mitral valve. This improves the patient’s quality of life and reduces the risk of complications.
Mitral Valve Repair Techniques
Mitral valve repair is a surgical technique that involves fixing the damaged valve. This approach is preferred when possible. It preserves the patient’s own valve tissue, reducing the need for long-term anticoagulation therapy.
The repair techniques include:
- Annuloplasty: Repairing the ring-like structure around the valve.
- Leaflet repair: Fixing the leaflets of the valve.
- Chordal repair: Adjusting the chords that support the valve leaflets.
Mitral Valve Replacement Options
In cases where the mitral valve is severely damaged, replacement may be necessary. There are two main types of prosthetic valves used for replacement: mechanical valves and bioprosthetic valves.
Mechanical valves are durable but require lifelong anticoagulation therapy to prevent blood clots. Bioprosthetic valves, made from animal tissue, have a lower risk of clotting. They may need replacement after 10 to 15 years.
Minimally Invasive Approaches
Minimally invasive cardiac surgery is a technique that involves smaller incisions than traditional open-heart surgery. This approach can reduce recovery time and minimize scarring.
Some of the benefits of minimally invasive mitral valve surgery include:
- Less postoperative pain
- Shorter hospital stay
- Faster return to normal activities
Minimally invasive approaches are considered on a case-by-case basis. They depend on the patient’s overall health and the complexity of the valve disease.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Treatment
Recovery and rehabilitation are key parts of treating Mitral Valve Insufficiency. They ensure patients reach their best health outcomes. A good recovery plan helps patients regain strength, manage symptoms, and enhance their quality of life.
Post-Surgical Care
Post-surgical care is a critical phase in the recovery process. Patients are advised to follow a specific regimen. This includes wound care, medication management, and monitoring for complications. In countries with advanced medical facilities like Turkey, the quality of care is exceptionally high. This contributes to a smoother recovery.
Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
Cardiac rehabilitation programs are vital in the recovery process. They include exercise training, education on heart-healthy living, and stress management. These programs help patients regain strength, reduce symptoms, and improve cardiovascular health.
Long-term Recovery Expectations
Long-term recovery expectations vary based on the condition’s severity, treatment type, and individual factors. Generally, patients see significant improvements in symptoms and quality of life. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Complications of Untreated Mitral Valve Insufficiency
Mitral Valve Insufficiency, if left untreated, can lead to a multitude of serious health complications. It affects not just the heart but also has broader implications for overall health and well-being.
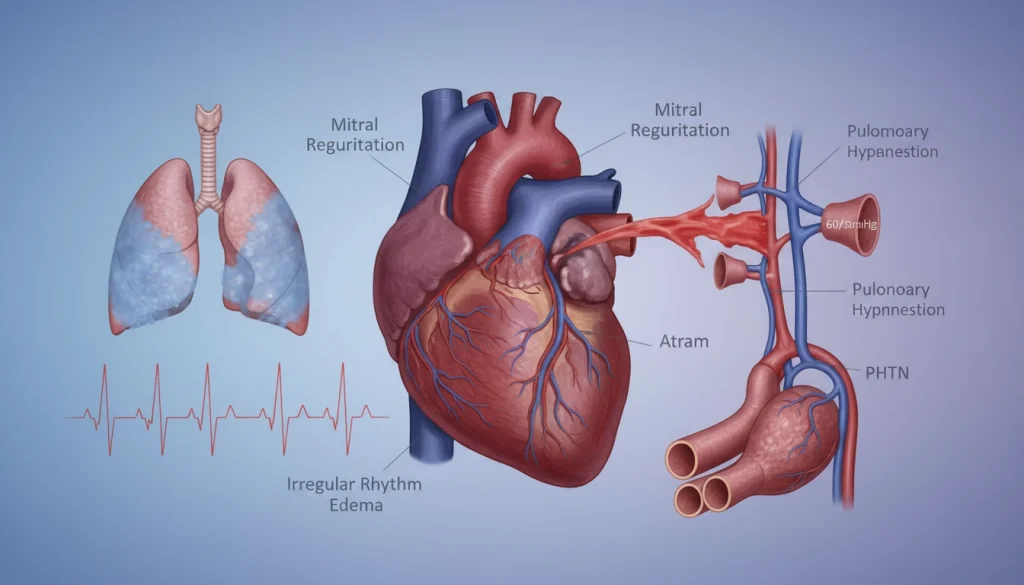
Cardiac Complications
Untreated Mitral Valve Insufficiency can lead to cardiac complications. Heart failure, where the heart can’t pump enough blood, is a major concern. Arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats, can also compromise cardiac function further.
Systemic Effects
Mitral Valve Insufficiency’s effects extend beyond the heart. Inefficient blood circulation can cause fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling in the legs and feet. In severe cases, it can lead to pulmonary hypertension, where blood pressure in the lungs’ arteries becomes too high.
Impact on Quality of Life
The complications from untreated Mitral Valve Insufficiency can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. Symptoms like persistent fatigue and shortness of breath limit physical activity and daily functioning. The psychological impact of dealing with a chronic condition can also lead to anxiety and depression, further reducing quality of life.
Special Considerations for Different Populations
Managing Mitral Valve Insufficiency (MVI) requires special attention for children, pregnant women, and the elderly. Each group has unique physiological traits and health needs. These factors influence diagnosis, treatment, and management of MVI.
Mitral Valve Insufficiency in Children
MVI in children can stem from congenital or acquired causes. Congenital heart defects are a common reason for MVI in this age group. Pediatric cardiac surgery is often necessary to address these defects. The treatment plan must account for the child’s growth and development.
- Regular monitoring by a pediatric cardiologist
- Potential need for surgical intervention
- Considerations for endocarditis prophylaxis
Management During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can exacerbate Mitral Valve Insufficiency due to increased blood volume and cardiac output. Women with pre-existing MVI need close monitoring by both a cardiologist and an obstetrician. The management plan should be tailored to the individual’s condition, possibly involving medication adjustments and activity level modifications.
- Pre-pregnancy counseling for women with known MVI
- Regular cardiac evaluations during pregnancy
- Planning for delivery, considering the cardiac condition
Considerations for Elderly Patients
Elderly patients with Mitral Valve Insufficiency often face challenges due to comorbid conditions. The presence of other heart diseases, like coronary artery disease, can influence treatment options. A thorough geriatric assessment is essential in determining the most appropriate course of action.
- Comprehensive assessment of comorbid conditions
- Consideration of surgical risk versus benefit
- Optimization of medical management
Living with Mitral Valve Insufficiency
Managing Mitral Valve Insufficiency in daily life demands a holistic approach. It involves medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support. This combination is key to effectively handling the condition.
Daily Management Strategies
Effective daily management of Mitral Valve Insufficiency includes several steps:
- Monitoring symptoms and reporting any changes to your healthcare provider
- Adhering to prescribed medication regimens
- Making necessary lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and appropriate exercise
Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider are essential. They help in adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Emotional and psychological support is critical for those with Mitral Valve Insufficiency. This support can be found through:
- Support groups, either in-person or online, to connect with others who have the condition
- Counseling or therapy to address anxiety, depression, or other mental health concerns
- Family and friends who can provide emotional support and help with daily tasks
Advances in Understanding and Treating Mitral Valve Insufficiency
Recent years have brought significant progress in understanding and treating Mitral Valve Insufficiency. This condition occurs when the mitral valve fails to close properly, causing mitral regurgitation. These advancements have greatly improved patient outcomes and overall quality of life.
Minimally invasive surgical techniques have emerged as a major breakthrough. They significantly reduce recovery time and minimize scarring. The field of mitral valve repair and replacement has also evolved, incorporating advanced materials and technologies.
Diagnostic imaging has seen major improvements, with 3D echocardiography leading the way. This technology allows healthcare providers to accurately assess the severity of mitral regurgitation. It aids in planning the most suitable treatment. New pharmaceuticals have also been developed, expanding medical management options for those with Mitral Valve Insufficiency.
Looking ahead, research is expected to drive further innovations in treating Mitral Valve Insufficiency. Future advancements are likely to include more sophisticated surgical techniques, device therapy, and personalized medicine approaches. These developments promise to enhance patient outcomes and alleviate the condition’s impact.
FAQ
Q: What is Mitral Valve Insufficiency?
A: Mitral Valve Insufficiency, also known as mitral regurgitation, occurs when the mitral valve fails to close properly. This failure allows blood to flow backward in the heart.
Q: What are the symptoms of Mitral Valve Insufficiency?
A: Symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, palpitations, and swelling in the legs and feet. In severe cases, it can lead to heart failure.
Q: How is Mitral Valve Insufficiency diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a physical examination, echocardiography, and other imaging tests. Laboratory tests also assess heart function.
Q: What are the treatment options for Mitral Valve Insufficiency?
A: Treatment options include medical management with medications and lifestyle modifications. Surgical interventions, like mitral valve repair or replacement, are also available.
Q: Can Mitral Valve Insufficiency be managed without surgery?
A: Yes, mild to moderate cases can be managed with medications and lifestyle changes. Severe cases may require surgical intervention.
Q: What is the difference between mitral valve repair and replacement?
A: Mitral valve repair fixes the existing valve. Replacement involves substituting it with a mechanical or bioprosthetic valve.
Q: Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage Mitral Valve Insufficiency?
A: Yes, maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress can help manage the condition.
Q: Can Mitral Valve Insufficiency lead to complications if left untreated?
A: Yes, untreated Mitral Valve Insufficiency can lead to serious complications. These include heart failure, arrhythmias, and pulmonary hypertension.
Q: How often should I have follow-up appointments if I have Mitral Valve Insufficiency?
A: Follow-up appointment frequency depends on the condition’s severity and treatment plan. Regular monitoring is essential for effective management.
Q: Is Mitral Valve Insufficiency a common condition?
A: Yes, it is one of the most common valvular heart diseases. Its prevalence increases with age.
Q: Can Mitral Valve Insufficiency be a sign of an underlying condition?
A: Yes, it can be associated with various underlying conditions. These include degenerative disorders, rheumatic heart disease, and infective endocarditis.