Polyneuropathy: What is Polyneuropathy?
Polyneuropathy is a condition that impacts the peripheral nerves, causing nerve damage. This leads to a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain and disability. It affects the body’s ability to function normally. The peripheral nerves are vital for controlling the body’s functions. These include movement, sensation, and organ function. Damage to these nerves disrupts the body’s normal functioning, leading to significant health issues.
Understanding polyneuropathy is key to effective diagnosis and management. This article aims to provide an overview of the condition. It covers its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. The goal is to educate readers on managing and coping with nerve damage. Polyneuropathy is a condition where multiple peripheral nerves malfunction simultaneously. It can stem from various causes and show different symptoms. To grasp polyneuropathy, we must understand its definition, the mechanisms behind it, and its impact on the peripheral nervous system.
Definition and Basic Mechanism
Polyneuropathy involves widespread damage to peripheral nerves. This damage can result from metabolic disorders, infections, or toxin exposure. The condition disrupts nerve cells’ ability to send signals. This disruption can harm the nerve’s axon, myelin sheath, or both, causing a variety of neurological symptoms.
Peripheral Nervous System Overview
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) extends from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. It transmits signals between the central nervous system and the body, controlling both voluntary and involuntary actions. Damage to the PNS, as seen in polyneuropathy, can severely impact these functions, leading to significant morbidity.
Peripheral nerves can be affected in different ways, leading to various types of polyneuropathy. These include sensory, motor, and autonomic neuropathies. Each type has unique symptoms based on the nerves affected.
Types of Polyneuropathy
Grasping the various forms of polyneuropathy is key to managing and treating it effectively. This condition can be classified by its duration, the underlying pathology, and the nerves it impacts.
Acute vs. Chronic Polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy can manifest as either acute or chronic. Acute forms develop swiftly, sometimes within days or weeks, and are commonly seen in conditions like Guillain-Barré Syndrome. In contrast, chronic polyneuropathy evolves gradually, spanning months or years, and is frequently associated with diabetes, nutritional deficiencies, or genetic predispositions.
Acute cases necessitate prompt medical intervention due to the high risk of rapid deterioration and severe complications. Management of chronic polyneuropathy aims to slow disease progression and mitigate symptoms.
Axonal vs. Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy can further be distinguished into axonal and demyelinating forms. Axonal polyneuropathy damages the axons, disrupting nerve signals. Demyelinating polyneuropathy, on the other hand, impacts the myelin sheath, hindering nerve conduction.
Axonal damage is prevalent in toxic and metabolic disorders. Demyelinating polyneuropathy, characteristic of conditions like Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, affects the myelin sheath.
Sensory, Motor, and Autonomic Polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy can target different nerve types, resulting in sensory, motor, or autonomic symptoms. Sensory polyneuropathy manifests as pain, numbness, or tingling. Motor polyneuropathy causes muscle weakness and atrophy. Autonomic polyneuropathy impacts involuntary functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and blood pressure.
Many instances of polyneuropathy combine these symptom types, making diagnosis and treatment more complex.
Common Causes of Polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy can stem from several factors, including metabolic disorders and autoimmune conditions. Grasping these causes is key to diagnosing and managing the condition effectively.
Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders
Diabetes is a leading cause of polyneuropathy, known as diabetic neuropathy. Prolonged high blood sugar levels can harm nerves, causing numbness, pain, and weakness in limbs.
Other metabolic disorders, like hypothyroidism and uremia, also contribute to polyneuropathy.
Autoimmune Conditions
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Guillain-Barré Syndrome can cause polyneuropathy.
In these cases, the immune system damages nerves, disrupting their function and causing symptoms.
Toxic and Medication-Induced Polyneuropathy
Certain toxins and medications can induce polyneuropathy. Chemotherapy drugs, some antibiotics, and industrial chemicals can harm nerves.
Excessive alcohol consumption also leads to alcoholic neuropathy, a form of polyneuropathy.
In conclusion, polyneuropathy has multiple causes, including diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and exposure to toxins or certain medications. Understanding these causes is vital for effective diagnosis and treatment.
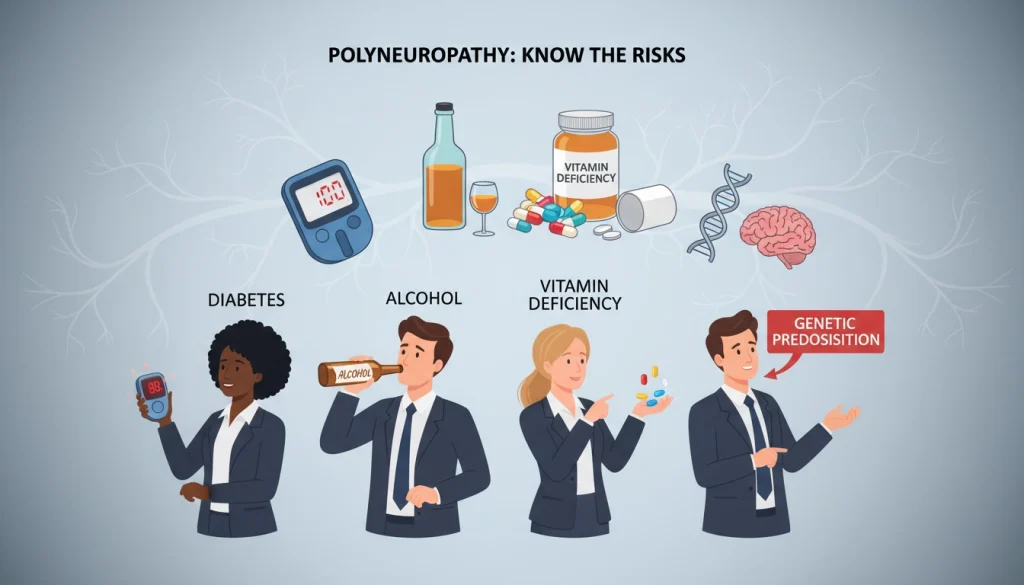
Risk Factors for Developing Polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy’s development is shaped by genetic, age-related, and environmental factors. Recognizing these risk factors is key to spotting those at higher risk. It may also help prevent the condition from occurring.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics significantly influence certain polyneuropathy types. Some people inherit conditions like Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, affecting peripheral nerves. Family history often indicates a higher risk of these conditions.
Age-Related Factors
Age is a major risk factor for polyneuropathy. The risk grows after 40, due to nerve toxin exposure and natural aging. This affects nerve health over time.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle and environment also play a role in polyneuropathy risk. Toxins, certain drugs, and nutritional deficiencies harm nerves. Diabetes, linked to lifestyle, greatly increases polyneuropathy risk.
Recognizing Polyneuropathy Symptoms
Identifying the various symptoms of polyneuropathy is vital for both patients and healthcare professionals. This condition can present in many ways, mainly categorized into sensory, motor, and autonomic symptoms.
Sensory Symptoms
Sensory symptoms often emerge first in polyneuropathy. These include numbness, tingling, or a pins-and-needles feeling, usually starting in the hands and feet. Patients may also experience pain, ranging from mild to severe, described as burning, stabbing, or aching.
Motor Symptoms
Motor symptoms affect the muscles, leading to weakness, wasting, or twitching. As the condition worsens, patients may struggle with walking or fine motor tasks due to muscle weakening.
Autonomic Symptoms
Autonomic symptoms impact the autonomic nervous system, controlling involuntary functions. Symptoms include orthostatic hypotension, gastrointestinal issues, and abnormal sweating. These symptoms can greatly affect a patient’s quality of life.
It’s critical to understand these symptoms for early detection and management of polyneuropathy. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, seeking medical advice is essential.
The Diagnostic Process for Polyneuropathy
Diagnosing polyneuropathy involves a detailed series of assessments to pinpoint the cause and extent of nerve damage. This process includes various tests and examinations. These aim to evaluate nerve function and identify the underlying causes.
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is key in diagnosing polyneuropathy. Healthcare professionals check muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation. This helps pinpoint areas of nerve damage and assess the condition’s severity.
Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography (EMG) are vital for diagnosing polyneuropathy. NCS measure nerve signal speed and strength. EMG, on the other hand, evaluates muscle electrical activity. These tests help distinguish between different types of neuropathy.
Blood Tests and Other Laboratory Investigations
Blood tests are conducted to uncover underlying causes of polyneuropathy. This includes checking for diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, or autoimmune disorders. Other tests, like urine and cerebrospinal fluid analysis, help rule out specific conditions.
Nerve Biopsy and Other Advanced Tests
In some cases, a nerve biopsy is performed to examine nerve tissue. Advanced tests, such as genetic testing or autonomic function tests, may also be used. These help diagnose specific types of polyneuropathy or assess autonomic nervous system involvement.
Conventional Medical Treatments
Managing polyneuropathy effectively requires a treatment plan that includes various medical interventions. These treatments aim to alleviate symptoms, slow disease progression, and enhance quality of life.
Pain Management Medications
Pain management is a key aspect of treating polyneuropathy. Several medications are used to reduce pain, including:
- Anticonvulsants like gabapentin and pregabalin
- Tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors like duloxetine
- Topical agents including lidocaine patches
These medications can help alleviate pain and improve sleep quality. Yet, they may have side effects, and their effectiveness can vary among individuals.
Disease-Modifying Treatments
In some instances, treatments aimed at modifying the disease can address the root cause of polyneuropathy. For example:
- Immunosuppressive therapies for autoimmune-related polyneuropathy
- Discontinuing or reducing the dosage of medications that may be causing neuropathy
- Treatment of underlying metabolic disorders, such as diabetes
Disease-modifying treatments aim to slow or halt the progression of polyneuropathy.
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is vital in managing polyneuropathy symptoms and improving functional ability. Techniques may include:
- Exercise programs to improve strength and flexibility
- Modalities such as heat, cold, or electrical stimulation to alleviate pain
- Assistive devices to aid mobility and balance
Physical therapy can help individuals with polyneuropathy maintain independence and enhance their overall quality of life.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Alongside traditional treatments, alternative and complementary therapies offer significant benefits for managing polyneuropathy. They can ease symptoms, enhance quality of life, and even slow disease progression. This approach is gaining popularity as it complements conventional methods.
Nutritional Supplements
Nutritional supplements can be a valuable addition for those with polyneuropathy. Vitamins and minerals like vitamin B12, alpha-lipoic acid, and omega-3 fatty acids may help manage symptoms and support nerve health. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.

Acupuncture and Massage
Acupuncture and massage are alternative therapies that may offer relief for polyneuropathy symptoms. Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific body points to stimulate healing and pain relief. Massage therapy can reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and promote relaxation.
Mind-Body Techniques
Mind-body techniques, including meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, can help manage stress and discomfort from polyneuropathy. These practices promote relaxation, improve mood, and enhance overall well-being.
Managing Polyneuropathy at Home
Managing polyneuropathy at home demands a holistic approach. It involves self-care, the use of adaptive equipment, and making safety modifications. These strategies help individuals with polyneuropathy enhance their quality of life and lower the risk of complications.
Daily Self-Care Strategies
Daily self-care is vital for managing polyneuropathy symptoms. This includes:
- Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule to help regulate nerve function
- Engaging in gentle exercises, such as yoga or swimming, to improve mobility and reduce pain
- Practicing stress-reducing techniques, like meditation or deep breathing
Adaptive Equipment and Assistive Devices
Adaptive equipment and assistive devices play a significant role in daily functioning for individuals with polyneuropathy.
- Canes or walkers to enhance mobility and balance
- Adaptive utensils for easier meal preparation
- Orthotic devices to support affected limbs
Home Safety Modifications
Modifying the home environment is critical to prevent falls and injuries.
Key modifications include:
- Removing tripping hazards, such as loose rugs or cords
- Installing handrails in strategic locations, like bathrooms and stairways
- Improving lighting to reduce the risk of falls
Preventing Polyneuropathy Progression
Managing polyneuropathy effectively requires several key strategies to halt its progression. By taking a proactive stance, individuals can enhance their quality of life and lower the risk of complications.
Blood Sugar Control for Diabetic Neuropathy
For those with diabetic neuropathy, controlling blood sugar levels is critical. This means monitoring blood glucose regularly, following a balanced diet, and sticking to prescribed medications. Keeping blood sugar within a target range can slow neuropathy’s progression and even reverse some damage.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Making healthy lifestyle choices is essential to prevent polyneuropathy from worsening. A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, like B vitamins, is vital for nerve health. Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can also help manage symptoms and boost overall health.
Regular Medical Monitoring
Regular medical check-ups are key for tracking polyneuropathy’s progression and adjusting treatments as needed. Healthcare providers can conduct nerve function tests, evaluate symptom severity, and offer guidance on effective management.
Living with Chronic Polyneuropathy
Chronic polyneuropathy brings a host of challenges that impact daily life, mental health, and overall well-being. It demands a holistic approach to manage its symptoms and its effects.
Coping Strategies for Daily Life
Effective coping strategies are essential for managing daily life with chronic polyneuropathy. This includes pacing activities, using adaptive equipment, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Simple adjustments, such as taking regular breaks and practicing relaxation techniques, can significantly improve quality of life.
Mental Health Considerations
The psychological impact of chronic polyneuropathy should not be underestimated. Individuals may experience anxiety, depression, or frustration due to their condition. Seeking support from mental health professionals, support groups, or loved ones is vital for maintaining mental well-being.
Work and Social Life Adjustments
Chronic polyneuropathy often necessitates adjustments in work and social life. This may involve modifying job responsibilities, exploring new career paths, or finding new hobbies that accommodate physical limitations. Maintaining social connections and engaging in activities that bring joy can help individuals cope with the condition.
By adopting these strategies and seeking support, individuals with chronic polyneuropathy can improve their quality of life and navigate the challenges associated with the condition.
Special Considerations for Different Age Groups
Understanding polyneuropathy’s effects on different age groups is key to effective management and treatment. This condition impacts people across various demographics, requiring tailored approaches for each age group.
Polyneuropathy in Children and Young Adults
In children and young adults, polyneuropathy can hinder developmental milestones and quality of life. Early diagnosis and intervention are vital to prevent long-term effects. Treatment for this age group involves a multidisciplinary approach. This includes physical therapy, occupational therapy, and psychological support to address their unique challenges.
Polyneuropathy in Older Adults
Older adults are more susceptible to polyneuropathy due to factors like diabetes, nutritional deficiencies, and toxin exposure. Managing this condition in older adults requires careful consideration of comorbidities and drug interactions. Treatment strategies focus on symptom management, improving mobility, and boosting quality of life.

When to Seek Medical Attention
Polyneuropathy demands prompt medical attention in specific situations. Being aware of these can be lifesaving. While managing polyneuropathy involves long-term care and lifestyle adjustments, there are critical moments for immediate medical evaluation.
Warning Signs and Red Flags
Certain symptoms signal the need for urgent medical evaluation. These include:
- Progressive weakness or numbness in the limbs
- Increasing difficulty with walking or balance
- Severe pain that is not managed with current treatments
- Symptoms that worsen over time
Recognizing these warning signs early can lead to timely interventions. These may improve outcomes significantly.
Emergency Symptoms
In some cases, polyneuropathy symptoms can escalate to emergencies. These include:
- Sudden onset of severe weakness or paralysis
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
If you or someone you know is experiencing these emergency symptoms, immediate medical care is essential.
Complications of Untreated Polyneuropathy
Untreated polyneuropathy can lead to a multitude of complications that significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. These complications can be far-reaching, affecting not only physical health but also emotional and social well-being.
Physical Complications
Physical complications of untreated polyneuropathy can be severe. They include:
- Muscle weakness and wasting
- Increased risk of falls and injuries
- Chronic pain
- Sensory loss, potentially leading to unnoticed injuries
These physical complications can significantly impair an individual’s ability to perform daily activities.
Quality of Life Impact
The impact of untreated polyneuropathy on quality of life is substantial. It can lead to:
- Emotional distress, including depression and anxiety
- Social isolation due to decreased mobility and chronic pain
- Reduced independence in daily life
- Potential loss of employment or significant changes in work life
Addressing polyneuropathy early is critical to preventing these complications and maintaining a good quality of life.
Current Research and Advances in Polyneuropathy Treatment
The field of polyneuropathy research is rapidly evolving. Emerging therapies and clinical trials are leading to better patient outcomes. Researchers are working hard to understand the causes of polyneuropathy and find more effective treatments.
Recent studies have focused on identifying new therapeutic targets and developing innovative treatment approaches. These advances are essential for addressing the complex nature of polyneuropathy. They aim to improve the quality of life for those affected.
Emerging Therapies
Emerging therapies in polyneuropathy treatment include gene therapy, stem cell therapy, and novel pharmacological agents. Gene therapy targets the genetic causes of certain types of polyneuropathy. Stem cell therapy aims to repair or replace damaged nerve cells. Novel pharmacological agents are being developed to target specific pathways involved in the disease process.
These emerging therapies hold promise for providing more targeted and effective treatments for polyneuropathy patients. As research progresses, we can expect to see more treatment options available.
Clinical Trials and Research Participation
Clinical trials are vital for advancing polyneuropathy treatment. They provide a controlled environment to test new therapies and assess their safety and efficacy. Participation in clinical trials is essential for the development of new treatments and for patients to access cutting-edge therapies.
Patients interested in participating in clinical trials should discuss their options with their healthcare provider. Many research studies are currently recruiting participants. There are resources available to help patients find relevant trials.
Resources and Support for People with Polyneuropathy
Those dealing with polyneuropathy can tap into a wealth of resources and support. Organizations like the Neuropathy Foundation and the American Diabetes Association provide essential information and community connections. They offer guidance tailored to those facing this condition.
Support groups, both online and in-person, serve as a vital platform. They allow individuals to share their experiences and receive emotional support. This exchange helps in learning from others who face similar challenges. Online forums and social media groups also offer comfort and practical advice.
Healthcare providers and neurologists play a key role. They offer personalized recommendations for managing polyneuropathy. This includes access to physical therapy, pain management specialists, and other supportive care services.
By utilizing these resources, individuals can better manage their condition. They can improve their quality of life and find the necessary support to manage symptoms effectively.
FAQ
Q: What is polyneuropathy?
A: Polyneuropathy is a condition affecting the peripheral nerves. It leads to numbness, weakness, and pain.
Q: What are the common causes of polyneuropathy?
A: Causes include diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and toxic or medication-induced neuropathy. Genetic predisposition also plays a role.
Q: How is polyneuropathy diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a physical exam and nerve conduction studies. EMG, blood tests, and nerve biopsy are also used.
Q: What are the symptoms of polyneuropathy?
A: Symptoms include numbness, tingling, weakness, and pain. Changes in heart rate or blood pressure are also common.
Q: How is polyneuropathy treated?
A: Treatment includes pain management and disease-modifying treatments. Physical therapy and alternative therapies like supplements and acupuncture are also used.
Q: Can polyneuropathy be prevented?
A: Preventing progression involves controlling blood sugar for diabetic neuropathy. Healthy lifestyle choices and regular monitoring are key.
Q: How does polyneuropathy affect daily life?
A: It impacts daily life, requiring coping strategies and mental health considerations. Adjustments to work and social life are necessary.
Q: Are there any resources available for people with polyneuropathy?
A: Yes, resources include organizations, support groups, and online resources. They provide information and support for managing the condition.