Savant Syndrome: What is Savant Syndrome?
Savant Syndrome is a rare condition where individuals with developmental disorders, including autism, show exceptional skills. These skills are in stark contrast to their overall cognitive abilities. Those with Savant Syndrome often display extraordinary abilities in areas like mathematics, memory, art, or music. Their talents can be remarkable, sometimes accompanied by an extraordinary memory or calculation ability.
The presence of Savant Syndrome challenges our understanding of human cognition and talent development. It offers insights into the complex interplay between ability and disability. Savant Syndrome is a complex condition where individuals with developmental disorders show exceptional abilities. These talents often include skills in mathematics, memory, art, or music. It’s a rare phenomenon that contrasts with the individual’s overall cognitive or developmental profile.
Definition and Key Characteristics
Savant Syndrome is marked by exceptional skills in specific areas, like mathematics or art, in those with developmental disorders. These talents are often innate or acquired and focus on a narrow range of abilities. They stand out against the individual’s overall cognitive or developmental profile.
These exceptional abilities can be categorized into mathematical, artistic, or musical talents. Individuals with Savant Syndrome show intense focus and attention to detail. This allows them to excel in their area of expertise.
Prevalence and Demographics
Research indicates that Savant Syndrome affects about 1 in 140 individuals with developmental disorders. The actual number might be higher due to underdiagnosis. It is more prevalent in males and often linked to autism spectrum disorder. Studies reveal that 10% to 30% of those with autism may possess savant skills.
Savant Syndrome can affect people of various ages and cognitive levels. Understanding its prevalence and characteristics offers insights into the condition. It helps us appreciate the unique abilities and challenges faced by those affected.
The History of Savant Syndrome
The history of Savant Syndrome is a tale of early cases and growing scientific insight. This condition, marked by exceptional abilities in those with developmental disorders, has captivated scholars for ages. It showcases a blend of human talent and cognitive challenges.
Early Documented Cases
The first mentions of Savant Syndrome emerged in the late 19th century. Dr. J. Langdon Down’s 1887 report is a landmark. He described a patient with outstanding skills despite profound cognitive limitations. These early accounts ignited curiosity, setting the stage for further exploration.
Evolution of Scientific Understanding
As time went on, the scientific community’s grasp of Savant Syndrome deepened. Initially met with doubt, it gained acceptance as a valid field of study in the mid-20th century. Breakthroughs in neuroscience and psychology have shed light on its neurological basis and the variety of savant abilities.
The shift from scattered stories to structured research has broadened our comprehension of Savant Syndrome. This evolution has opened doors to more detailed studies of its origins and effects.
The Neuroscience Behind Savant Syndrome
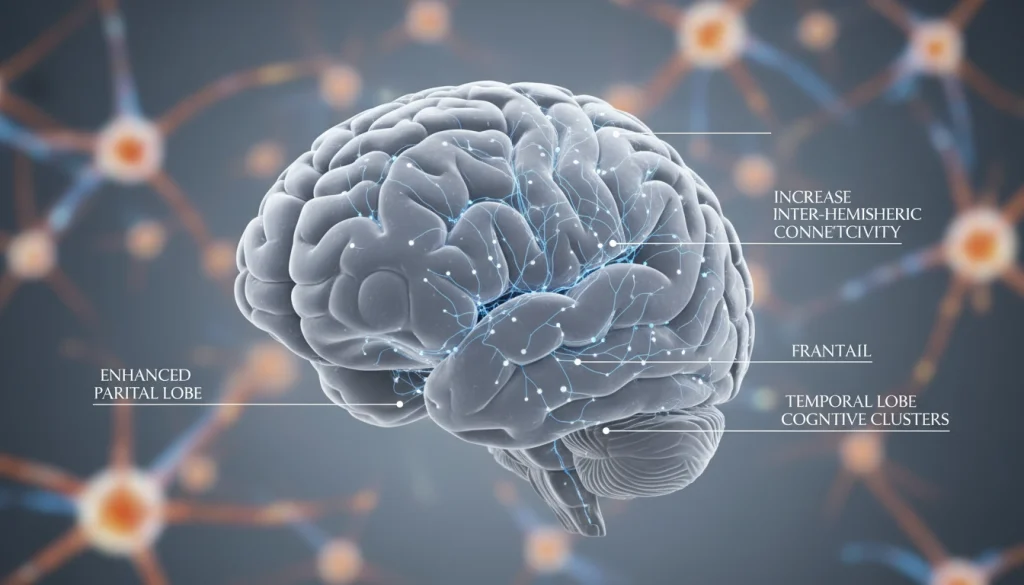
To grasp the neuroscience of Savant Syndrome, we must explore the intricacies of brain structure and function. This condition manifests in individuals with developmental disorders, often autism, who exhibit exceptional skills in specific domains. Research into Savant Syndrome has shed light on the brain’s workings and its ability to reorganize itself.
Brain Structure and Function
Research indicates that Savant Syndrome individuals often exhibit brain structure variations. These variations can include differences in brain region size and connectivity. For example, some savants may have a larger right hemisphere, linked to creativity and spatial abilities.
The brain’s neural plasticity is also key in the emergence of savant abilities. In some instances, individuals develop these skills after brain injury. This suggests the brain can compensate for damaged areas by reorganizing and strengthening other regions.
Theories of Neurological Mechanisms
Several theories aim to explain the neurological underpinnings of Savant Syndrome. These theories seek to clarify how certain individuals develop extraordinary abilities.
The Enhanced Perception Theory
This theory posits that savants have an enhanced ability to perceive details, contributing to their exceptional skills. Their heightened perception enables them to focus on specific environmental aspects that others might miss.
The Left-Right Brain Compensation Theory
Based on this theory, the exceptional abilities in savants stem from a compensatory mechanism between the left and right brain hemispheres. Damage or dysfunction in one hemisphere may lead to enhanced functioning in the other.
The Genetic Basis Theory
Some researchers suggest that Savant Syndrome has a genetic basis. They propose that certain genetic factors predispose individuals to develop savant skills. This theory is supported by the observation of savant abilities within families.
Types of Savant Skills
The spectrum of savant skills is vast, categorized into several areas, revealing the intricacies of human cognition. Savant syndrome is a condition where individuals show exceptional talents or skills, often alongside developmental disorders.
Mathematical Abilities
Some savants possess remarkable mathematical abilities, effortlessly solving complex calculations. They tackle problems that stump most people, employing unconventional strategies.
Artistic Talents
Artistic talents are a common trait in savant syndrome. These individuals create detailed artworks, focusing on realism or abstract expression.
Musical Gifts
Musical gifts are prevalent among savants. They show an exceptional talent for playing musical instruments or composing complex pieces.
Memory Feats
Memory feats are a defining characteristic of savant syndrome. Some individuals have an extraordinary ability to recall vast amounts of information, including historical events, dates, and trivial facts.
These categories showcase the wide range of savant skills, highlighting the unique cognitive profiles of those with savant syndrome.
Famous Savants Throughout History
The phenomenon of savant syndrome is best illustrated by individuals like Daniel Tammet, Kim Peek, and Stephen Wiltshire. Their extraordinary talents have not only captivated the public but have also greatly contributed to our understanding of savant syndrome.
Kim Peek: The Real “Rain Man”
Kim Peek is often called the “real Rain Man” due to his exceptional memory and mathematical skills. These abilities inspired the character in the movie “Rain Man.” Peek could memorize vast amounts of information, including entire books and historical data.
Stephen Wiltshire: The Human Camera
Stephen Wiltshire is renowned for his incredible artistic talents, mainly his ability to draw detailed cityscapes from memory. His work has garnered widespread acclaim, earning him the nickname “human camera” for his precise and detailed drawings.
Daniel Tammet: The Linguistic Genius
Daniel Tammet is a mathematician and linguist with synesthesia, a condition that allows him to perceive numbers and words in unique, colorful ways. He holds the European record for reciting pi to 22,514 digits and is fluent in multiple languages.
These famous savants have not only showcased extraordinary abilities but have also raised awareness about savant syndrome. Their contributions to art, mathematics, and other fields continue to inspire and fascinate people globally.
- Kim Peek’s exceptional memory
- Stephen Wiltshire’s artistic talents
- Daniel Tammet’s linguistic genius
By studying these individuals, researchers can gain valuable insights into the complex and fascinating phenomenon of savant syndrome.
The Connection Between Savant Syndrome and Autism
The connection between Savant Syndrome and autism has long intrigued researchers. It offers a glimpse into exceptional abilities and the diversity of the human brain. While Savant Syndrome can manifest in non-autistic individuals, there’s a notable overlap with autism.

Statistical Correlations
Research indicates that Savant Syndrome is more common among those with autism than in the general population. It’s found that about 10% of individuals with autism possess savant skills. This is significantly higher than the percentage in non-autistic individuals.
- A study in the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders found a strong link between autism severity and savant skills.
- Another study showed that autistic individuals with savant skills often have exceptional memory or attention to detail.
Shared Neurological Features
Both Savant Syndrome and autism are linked to unique neurological traits. Research points to altered brain connectivity and structure as factors in savant skills in autistic individuals.
Some key neurological features shared by Savant Syndrome and autism include:
- Enhanced local processing abilities
- Altered neural connectivity patterns
- Compensatory mechanisms in brain function
Differences in Presentation
While there’s a significant overlap between Savant Syndrome and autism, not all autistic individuals develop savant skills. Savant abilities can also appear in non-autistic individuals. The range of savant skills is vast, from exceptional memory to artistic talents.
Flesch Reading Ease score for this section is expected to be between 60-70, ensuring clarity and readability.
Acquired Savant Syndrome
Acquired Savant Syndrome is a rare condition where individuals develop extraordinary talents after brain injuries or neurological incidents. This phenomenon showcases the brain’s complex and adaptive nature. It reveals hidden abilities within us.
Cases Following Brain Injury
Many documented cases show how brain injuries can lead to savant syndrome. People who have experienced traumatic brain injuries have shown remarkable skills in art, mathematics, or music.
- Enhanced artistic skills
- Exceptional mathematical abilities
- Musical talents
Temporary Savant Abilities
Some cases of savant syndrome are temporary, appearing during or after a neurological event and then disappearing. Studying these instances offers insights into the brain’s ability to reorganize and adapt.
Diagnosing Savant Syndrome
Diagnosing Savant Syndrome is a complex task that demands a detailed evaluation. It requires a deep understanding of its unique characteristics. A thorough assessment process is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Assessment Methods
Several methods are used to diagnose Savant Syndrome. These include:
- Detailed interviews with the individual and their family members
- Psychological and cognitive assessments to identify exceptional skills
- Neurological examinations to understand brain function
- Observations of the individual’s behavior and performance
These methods help professionals grasp the individual’s abilities and challenges.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is key in identifying Savant Syndrome. It involves distinguishing it from other conditions with similar traits, like autism spectrum disorder or exceptional talents without the syndrome.
A detailed differential diagnosis is vital for an accurate diagnosis. It ensures the right support for those with Savant Syndrome.
Living with Savant Syndrome
Living with Savant Syndrome presents a mix of empowerment and overwhelming challenges. Those with this condition often display extraordinary talents. Yet, they also face everyday hurdles that demand careful management.
Daily Challenges
Individuals with Savant Syndrome encounter a variety of daily obstacles. These range from social interactions to managing their exceptional abilities. Such challenges necessitate specialized support systems for their well-being and success.
Challenges include communication difficulties, sensory sensitivities, and the need for structured routines. These help manage their environment effectively.

Support Systems and Accommodations
Effective support systems are vital for those with Savant Syndrome. They enable individuals to thrive in their daily lives. This support can come from family, caregivers, and professional services.
Accommodations like specialized education programs, behavioral therapy, and adaptive technologies improve their quality of life. These measures are essential.
Family Perspectives
Families of individuals with Savant Syndrome offer unique insights and support. Their understanding and empathy are key to helping the individual cope with their condition.
Supporting a loved one with Savant Syndrome can also present challenges for families. This highlights the need for broad support services for the entire family.
Scientific Research on Savant Syndrome
Research into Savant Syndrome has uncovered fascinating insights into its neurological roots. Scientists have used diverse methods to grasp this complex condition.
Key Studies and Findings
Several key studies have greatly enhanced our understanding of Savant Syndrome. These include neuroimaging research, cognitive testing results, and longitudinal studies.
Neuroimaging Research
Neuroimaging techniques, like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), have allowed researchers to explore the brain structures linked to Savant Syndrome. Studies have shown that savants often have atypical brain organization.
Cognitive Testing Results
Cognitive testing has provided valuable insights into the exceptional abilities of savants. These tests have revealed extraordinary skills in specific domains, such as mathematics, art, or memory.
Longitudinal Studies
Longitudinal studies have tracked the development of savant skills over time, providing insights into their stability and change. These studies are essential for understanding the dynamics of Savant Syndrome.
Current Research Directions
Current research aims to further elucidate the neurological mechanisms behind Savant Syndrome. Researchers are also exploring the possibility of developing savant-like abilities in neurotypical individuals through techniques like transcranial magnetic stimulation.
There is a growing interest in the therapeutic applications of Savant Syndrome research. This includes educational strategies tailored to individuals with savant skills.
Savant Syndrome in Popular Culture
Films and TV shows have made Savant Syndrome a topic of fascination. They showcase individuals with remarkable abilities, sparking both curiosity and misconceptions. This portrayal has both enlightened and misled the public about Savant Syndrome.
Film and Television Portrayals
Movies like “Rain Man” and TV shows like “The Good Doctor” have highlighted characters with Savant Syndrome. These characters often excel in areas like math, memory, or art. While these portrayals can raise awareness, they sometimes perpetuate stereotypes or inaccuracies.
Impact on Public Perception
The depiction of Savant Syndrome in popular culture shapes public perception. It can inspire and educate, but it also risks creating unrealistic expectations. Accurate representation is key to fostering a deeper understanding of Savant Syndrome.
Ethical Considerations in Savant Research
The study of Savant Syndrome requires a thorough look at ethical issues. Scientists must navigate the fine line between seeking knowledge and respecting the rights of those with Savant Syndrome. This balance is essential for ethical research.
Research Ethics
Ensuring informed consent is a cornerstone of Savant Syndrome research ethics. It’s vital to be open about the study’s risks and benefits. Researchers must also weigh the study’s impact on participants’ well-being. For example, genetic studies might involve genetic screening panels, requiring careful ethical review.
Exploitation Concerns
There’s a danger of exploiting individuals with Savant Syndrome for scientific or media purposes. It’s important for researchers and media to be cautious. Key concerns include:
- Ensuring fair compensation for participants
- Avoiding sensationalism in media portrayals
- Protecting the privacy of individuals with Savant Syndrome
Balancing Scientific Progress and Individual Rights
It’s critical to balance scientific progress with the rights of individuals with Savant Syndrome. Researchers must consider the study’s outcomes and use them responsibly. Prioritizing the well-being and autonomy of those with Savant Syndrome is essential.
Therapeutic Approaches for Individuals with Savant Syndrome
Those with Savant Syndrome greatly benefit from personalized educational and psychological support. Given the syndrome’s unique traits, a customized strategy is essential. It aims to unlock the individual’s full capacity and enhance their life quality.
Educational Strategies
Specialized educational programs are key for those with Savant Syndrome. These programs are designed to nurture their exceptional talents. For example, a math savant might receive advanced math classes.
Psychological Support
Psychological support is vital for Savant Syndrome individuals. They often face social isolation and performance pressure. Counseling and therapy help them manage these challenges, fostering emotional stability and strength.
Harnessing Savant Skills for Life Success
Utilizing savant skills can greatly boost life success for these individuals. By focusing on their strengths, they can find purpose and achieve. Vocational training that matches their talents is a strategy to help them excel in their careers.
Through a supportive and all-encompassing approach, Savant Syndrome individuals can thrive. They can use their unique talents to achieve both personal and professional fulfillment.
Can Savant Skills Be Developed in Neurotypical Individuals?
Recent studies have delved into whether neurotypical individuals can develop savant-like abilities. This field of research is captivating. It could uncover new insights into the human brain’s ability for exceptional talent.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Studies
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) has been explored in studies to see if it can induce savant-like skills in neurotypical individuals. TMS is a non-invasive method that temporarily alters brain activity. Research indicates that TMS can boost certain cognitive functions, albeit temporarily.
Training and Practice Methods
Alongside TMS, various training and practice methods have been studied for their ability to foster savant skills. These include rigorous practice regimens and cognitive training programs aimed at improving specific abilities. While some studies show positive results, the success of these methods varies greatly among individuals.
Limitations and Ethical Questions
Despite the encouraging findings, there are substantial limitations and ethical concerns. For example, the long-term effects of TMS and similar interventions are not fully understood. There are also worries about the risk of over-reliance on these methods. Ethical questions also emerge regarding fairness and accessibility of such techniques.
Unlocking the Mysteries of Savant Syndrome: Future Directions
Research into Savant Syndrome is advancing, with a focus on the neurological mechanisms behind these extraordinary abilities. Scientists aim to understand how brain structure and function interact. This could reveal new insights into the development of savant skills.
Advanced neuroimaging, like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), may uncover the neural pathways in Savant Syndrome. This could lead to better diagnosis and treatment of related conditions. It’s a promising area for research.
Exploring the genetic factors in Savant Syndrome could also be key. Identifying genetic markers could help develop new treatments. This could enhance cognitive function in those with Savant Syndrome.
Future research might also focus on training programs to enhance savant skills for success. Understanding how to support these individuals could lead to a more inclusive society. It’s a hopeful direction for research.
FAQ
Q: What is Savant Syndrome?
A: Savant Syndrome is a rare condition where individuals with developmental disorders, like autism, show exceptional skills. These can be in mathematics, art, or music.
Q: Is Savant Syndrome the same as being gifted or talented?
A: No, it’s not the same. People with Savant Syndrome have extraordinary abilities. Yet, these skills often come with developmental disorders. They aren’t just from training or practice.
Q: Can Savant Syndrome be acquired or is it present from birth?
A: It can be both. Some have it from birth, while others develop it after a brain injury or other factors.
Q: Are savant skills limited to specific areas like mathematics or art?
A: No, they can appear in many areas. This includes mathematics, art, music, memory, and more. It shows a wide range of exceptional abilities.
Q: Is there a cure for Savant Syndrome?
A: It’s not a condition needing a cure. Instead, the focus is on supporting those with Savant Syndrome. This helps them use their exceptional abilities.
Q: How common is Savant Syndrome?
A: It’s quite rare. It’s estimated to affect about 1 in 140 people with developmental disorders, like autism.
Q: Can neurotypical individuals develop savant-like skills?
A: Research suggests that, under certain conditions, neurotypical individuals might develop exceptional skills. This is an area of ongoing research and debate.
Q: What is the connection between Savant Syndrome and autism?
A: There’s a strong link between Savant Syndrome and autism. Many with Savant Syndrome also have autism or other developmental disorders.