Anatomy of the Temporomandibular Joint
Temporomandibular Joint Disorder, commonly referred to as TMJ Disorder, affects the jaw joint and surrounding muscles, causing pain and discomfort. This condition can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, making everyday activities like eating and speaking challenging. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for TMJ Disorder is key for effective management. The condition can result from various factors, including jaw injuries, teeth grinding, and arthritis. By recognizing the signs and symptoms, individuals can seek timely medical attention to alleviate their discomfort.
TMJ Disorder is a complex condition that requires a thorough approach to diagnosis and treatment. With the right care and attention, individuals can find relief from the symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Understanding Temporomandibular Joint Disorder
Temporomandibular Joint Disorder, commonly referred to as TMJ Disorder, affects the jaw joint and surrounding muscles. It’s a complex issue that can cause significant discomfort. This discomfort can disrupt daily life.
What Is TMJ Disorder?
TMJ Disorder involves pain and dysfunction in the temporomandibular joint. This joint connects the jawbone to the skull. Symptoms include jaw pain, clicking or popping sounds when opening or closing the mouth, and limited jaw movement.
Prevalence and Demographics
TMJ Disorder affects a significant portion of the population. Women are more likely to experience it than men. It can occur at any age but is most common among individuals between 20 and 40 years old.
Impact on Quality of Life
The impact of TMJ Disorder on an individual’s quality of life can be substantial. Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain. This pain affects eating, speaking, and even sleeping. Chronic TMJ Disorder can lead to emotional distress and decreased overall well-being.
Understanding the complexities of TMJ Disorder is key for effective management and treatment. Recognizing the signs and symptoms allows individuals to seek appropriate care. This can alleviate discomfort and improve their quality of life.
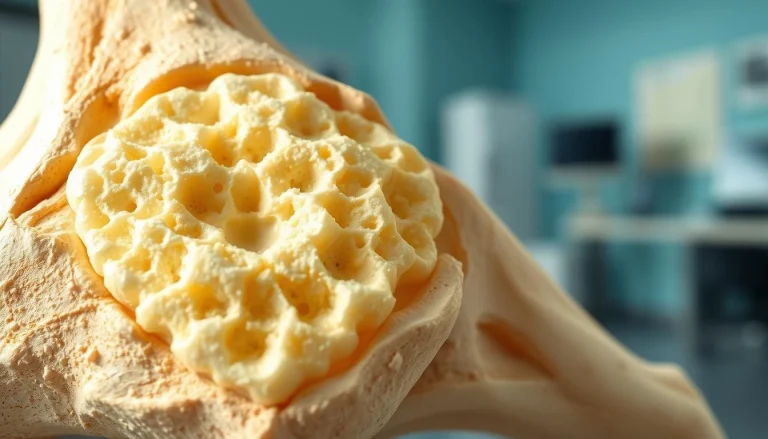
Anatomy of the Temporomandibular Joint
The Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) is a complex structure essential for jaw movement. It’s one of the most used joints in the human body. It plays a key role in daily activities like eating, speaking, and yawning.
Structure and Function
The TMJ is a synovial joint that links the mandible (lower jawbone) to the temporal bone of the skull. It consists of the articular eminence, the mandibular condyle, and the articular disc.
- The articular eminence is a bony ridge on the temporal bone.
- The mandibular condyle is the rounded end of the mandible.
- The articular disc is a fibrous cartilage structure that facilitates smooth movement.
How the TMJ Works
The TMJ enables the jaw to move in various directions. It allows for hinge movement for opening and closing, and gliding movement for sideways motions.
This complex movement is facilitated by the coordination between the TMJ’s bony components, the articular disc, and the surrounding muscles and ligaments.
Relationship to Surrounding Structures
The TMJ is closely related to surrounding facial structures. This includes the muscles of mastication (chewing), nerves, and blood vessels.
- The masseter and temporalis muscles are key in controlling jaw movement.
- The auriculotemporal nerve provides sensory innervation to the TMJ.
- The joint is also surrounded by a capsule that is rich in blood supply.
Causes of Temporomandibular Joint Disorder
Grasping the causes of TMJ Disorder is key to managing and treating it. TMJ Disorder often stems from a mix of physical, psychological, and dental factors. This multifaceted origin makes it challenging to address.
Physical Trauma and Injury
A blow to the face or a whiplash injury can trigger TMJ Disorder. Such injuries damage the joint and surrounding tissues. This damage leads to pain and dysfunction.
- Direct blows to the jaw
- Whiplash injuries
- Surgical complications
Bruxism and Teeth Grinding
Bruxism, or grinding and clenching teeth, significantly contributes to TMJ Disorder. This habit puts undue stress on the joint, causing inflammation and pain.
Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can worsen TMJ Disorder by causing jaw clenching or teeth grinding. Using relaxation techniques can help manage symptoms.
Arthritis and Inflammatory Conditions
Arthritis and other inflammatory conditions can impact the temporomandibular joint. They lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are common culprits.
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Other inflammatory joint diseases
Malocclusion and Dental Issues
Malocclusion, or teeth misalignment, can cause TMJ Disorder by unevenly stressing the joint. Dental problems, such as missing teeth or ill-fitting dental work, also contribute.
Understanding these causes helps individuals prevent TMJ Disorder and seek effective treatment. This approach is vital for managing the condition.
Risk Factors for Developing TMJ Disorder
TMJ Disorder is a complex condition influenced by various risk factors. Understanding these factors is key to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Genetic Predisposition
Research indicates that genetic factors may influence TMJ Disorder development. Those with a family history of TMJ issues are more likely to experience it.
Age and Gender Considerations
TMJ Disorder can affect anyone, but it’s more common in young adults and middle-aged individuals. Women are more prone to TMJ Disorder than men, pointing to a gender-related factor.
Occupational and Lifestyle Factors
Certain jobs and lifestyle choices can raise TMJ Disorder risk. For instance:
- Jobs requiring repetitive jaw movements or prolonged talking
- Habits like teeth grinding or clenching, often linked to stress
- Poor posture, affecting the head and neck
Pre-existing Medical Conditions
Pre-existing medical conditions can also increase TMJ Disorder risk. These include:
- Arthritis and other inflammatory conditions
- Conditions causing chronic pain or discomfort
- Previous jaw injuries or surgeries
Knowing these risk factors helps individuals take preventive steps and seek early treatment if symptoms appear.
Types and Classifications of Temporomandibular Joint Disorder
Grasping TMJ Disorder requires an understanding of its various forms and classifications. These distinctions are key to accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. TMJ Disorder includes several subtypes, each with unique characteristics and implications for management.
Myofascial Pain Dysfunction
Myofascial pain dysfunction is a prevalent TMJ Disorder type, marked by jaw muscle pain and inflammation. It often stems from muscle tension, teeth grinding, or other jaw strain causes.
Internal Derangement
Internal derangement occurs when the TMJ disc is out of alignment. This can cause jaw clicking, popping, or locking. It’s commonly accompanied by pain and restricted jaw movement.
Degenerative Joint Disease
Degenerative joint disease, like osteoarthritis, can afflict the TMJ, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced jaw function. This condition is more common in older adults or those with joint trauma history.
Combined or Complex TMJ Disorders
Some individuals face a mix of TMJ disorders, making diagnosis and treatment more complex. These cases demand a detailed treatment plan addressing all aspects of the condition.
Classifying TMJ Disorder into these categories aids healthcare providers in customizing diagnostic methods and treatment plans. This ensures each patient receives care tailored to their specific needs.
- Myofascial pain dysfunction involves muscle pain and inflammation.
- Internal derangement is characterized by disc misalignment within the TMJ.
- Degenerative joint disease affects the joint’s structure and function.
- Combined or complex disorders present a mix of these conditions.
Common Symptoms and Signs
Identifying the common symptoms of TMJ Disorder is key for proper diagnosis and treatment. TMJ Disorder shows through various symptoms, affecting an individual’s quality of life significantly.
Jaw Pain and Tenderness
Jaw pain or tenderness is a common symptom of TMJ Disorder. This discomfort can be constant or triggered by actions like chewing or yawning.
Clicking, Popping, and Grating Sounds
Many with TMJ Disorder hear clicking, popping, or grating sounds when moving their jaw. These sounds may be accompanied by jaw catching or locking sensations.
Limited Jaw Movement
TMJ Disorder can limit jaw movement. It makes it hard to open the mouth fully or move the jaw from side to side.
Referred Pain Patterns
The pain from TMJ Disorder isn’t just in the jaw. It can spread to other face and head areas, causing various pain patterns.
Headaches and Migraines
TMJ Disorder can cause frequent headaches or migraines. Jaw muscle tension can lead to pain that spreads to the head.
Ear Pain and Tinnitus
Ear pain or tinnitus (ringing in the ears) can occur due to TMJ’s proximity to ear structures.
Neck and Shoulder Discomfort
The tension and pain from TMJ Disorder can also affect the neck and shoulders. This adds to overall discomfort and stiffness.
Associated Symptoms
TMJ Disorder can also lead to symptoms like dizziness, tooth sensitivity, or a feeling of fullness in the ears.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Sensitivity of the teeth
- Fullness or pressure in the ears
Recognizing these symptoms is vital for a thorough diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
Diagnosis of Temporomandibular Joint Disorder
Healthcare professionals use various methods to diagnose Temporomandibular Joint Disorder. These include physical assessments and advanced imaging techniques. This approach ensures a thorough understanding of the condition, aiding in effective treatment planning.
Physical Examination
A detailed physical examination is the initial step in diagnosing TMJ Disorder. It involves checking the patient’s jaw movement and feeling the TMJ and surrounding muscles. Healthcare providers also look for pain or tenderness.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are vital in diagnosing TMJ Disorder. They offer detailed views of the joint’s structure and function.
-
X-rays
-
CT Scans
-
MRI
These tests help spot structural issues like bone spurs, fractures, or disc displacements. Such findings are key for an accurate diagnosis.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is critical in ruling out other conditions that might seem like TMJ Disorder. These include sinusitis, ear infections, or dental issues. A thorough review of symptoms and diagnostic results helps healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis.
Specialized TMJ Assessments
In some cases, specialized assessments like electromyography (EMG) and joint vibration analysis are used. These tests help evaluate TMJ function and dysfunction.
By combining these diagnostic methods, healthcare professionals gain a deep understanding of the patient’s condition. This understanding guides effective treatment strategies.
Medical Treatment Options
TMJ Disorder can be treated through various medical pathways, each with its own benefits and considerations. The choice of treatment hinges on the severity of symptoms, the disorder’s cause, and the patient’s health.
Medications
Medications are key in managing TMJ Disorder symptoms. The type of medication depends on the patient’s specific needs.
Pain Relievers and Anti-inflammatories
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen can reduce pain and inflammation. In severe cases, stronger prescription medications may be needed.
Muscle Relaxants
Muscle relaxants help alleviate muscle tension and pain in TMJ Disorder. They are beneficial for those with bruxism or teeth grinding.
Antidepressants
Antidepressants may be prescribed to manage chronic pain and symptoms like depression and anxiety.
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is a valuable option for TMJ Disorder. It focuses on exercises and techniques to improve jaw mobility and reduce pain.
- Jaw exercises to improve range of motion
- Manual therapy to relax the jaw muscles
- Posture correction to reduce strain on the TMJ
Oral Appliances and Splints
Oral appliances, including night guards and splints, are custom-made for the patient’s mouth. They help reduce teeth grinding and clenching, alleviating TMJ symptoms.

Injections and Minimally Invasive Procedures
For severe cases, injections and minimally invasive procedures can offer relief.
Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and pain in the TMJ.
Botox Treatments
Botox injections into the jaw muscles can relax them, reducing pain and tension.
Arthrocentesis
Arthrocentesis involves flushing out the joint with a sterile solution to reduce inflammation and improve function.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases where other treatments have failed, surgical options may be considered.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows for the examination and treatment of the TMJ.
Open-Joint Surgery
Open-joint surgery is a more invasive procedure used to repair or replace the TMJ.
Joint Replacement
In cases of severe joint damage, joint replacement surgery may be necessary.
Self-Care and Home Remedies
Self-care is vital for managing TMJ Disorder symptoms and improving life quality. By integrating simple yet effective self-care practices into daily life, individuals can better manage their condition. This approach helps in reducing discomfort.
Jaw Exercises and Stretches
Specific jaw exercises and stretches can enhance jaw mobility and lessen pain. Simple actions include opening and closing the mouth gently, moving the jaw from side to side, and doing chin tucks. These exercises should be done regularly but within a comfortable range to avoid worsening the condition.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to the affected area can offer relief from TMJ pain. Heat, like a warm washcloth, relaxes jaw muscles. Cold, such as an ice pack, reduces inflammation and numbs pain. Alternating between heat and cold is key to finding the best approach for each individual.
Dietary Modifications
Diet significantly impacts TMJ Disorder management. Making specific dietary changes can help minimize discomfort and prevent symptom worsening.
Soft Food Diet
Adopting a soft food diet reduces TMJ strain. Foods like yogurt, scrambled eggs, and cooked vegetables are recommended. Avoiding hard, sticky, or crunchy foods can alleviate pain and discomfort.
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can trigger or worsen TMJ symptoms. It’s wise to avoid hard, sticky, or wide-mouth opening foods like nuts, gum, and large sandwiches. Cutting food into smaller pieces and taking smaller bites can also reduce jaw stress.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress is a significant contributor to TMJ Disorder, often leading to teeth clenching and grinding. Practicing stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga, can lower stress levels. This can help alleviate TMJ symptoms.
Proper Posture and Ergonomics
Proper posture and ergonomics are essential for TMJ Disorder management. Ensuring workstations promote good posture and taking regular breaks to stretch are important. Being mindful of posture during daily activities can also reduce TMJ strain.
Complications of Untreated TMJ Disorder
Ignoring TMJ Disorder can lead to severe health issues and daily life challenges. If not treated, TMJ Disorder can cause a wide range of problems. These issues can significantly lower the patient’s quality of life.
Chronic Pain Development
Chronic pain is a major complication of untreated TMJ Disorder. Jaw pain can spread to the face, ears, neck, and shoulders. This creates a complex pain pattern that’s hard to manage.
Impact on Daily Activities
TMJ Disorder can greatly affect daily life. Pain and discomfort make eating, speaking, and even yawning hard. Simple tasks become difficult, reducing quality of life.
Psychological Effects
TMJ Disorder can also have psychological effects. Chronic pain and limitations can cause anxiety and depression. This affects mental health and overall well-being.
Progressive Joint Damage
Untreated TMJ Disorder can cause progressive joint damage. This leads to more severe pain and limited jaw movement. It creates a cycle of worsening that’s hard to reverse.
Sleep Disturbances
Sleep disturbances are another issue. Pain and discomfort make finding a comfortable sleeping position hard. This can lead to insomnia or other sleep problems. It worsens the condition, creating a vicious cycle.
In conclusion, the complications of untreated TMJ Disorder highlight the need for timely and proper treatment. This is to manage symptoms and prevent long-term damage.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Knowing when to seek medical help is essential for managing TMJ Disorder effectively. TMJ Disorder can present in various ways. Understanding the severity of your symptoms is critical in deciding when to consult a healthcare professional.
Warning Signs and Red Flags
Certain symptoms require immediate medical attention. These include severe jaw pain, jaw locking, difficulty chewing, and persistent clicking or grating sounds when opening or closing the mouth.
- Persistent pain or tenderness in the jaw, face, or surrounding areas
- Difficulty or pain while chewing
- Clicking, popping, or grating sounds when opening or closing the mouth
- Locking of the jaw joint
Finding the Right Specialist
Choosing the right healthcare professional is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment. Depending on your specific needs, you may be referred to different specialists.
Dentists and Oral Surgeons
Dentists and oral surgeons play a key role in diagnosing and treating TMJ Disorder. They are essential when dental issues or malocclusion are involved.
TMJ Specialists
TMJ specialists have advanced knowledge in treating TMJ disorders. They offer a range of treatment options tailored to your condition.
Pain Management Experts
Pain management experts can help manage chronic pain associated with TMJ Disorder. They provide relief and improve your quality of life.
Preparing for Your Appointment
Before your appointment, make a list of your symptoms. Include when they started and any factors that relieve or exacerbate them. This information will help your healthcare provider make an accurate diagnosis.
Recent Advances in TMJ Research and Treatment
New breakthroughs in TMJ research are changing how we diagnose and treat this complex issue. Recent years have brought a deeper understanding of temporomandibular joint disorder. This has led to more effective and tailored treatment options.
Emerging Therapies
The field of TMJ disorder treatment is seeing new, innovative therapies emerge. These include regenerative medicine and biofeedback technology, promising to transform patient care.
Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine, such as stem cell therapy and PRP injections, is being explored. It aims to repair and regenerate damaged TMJ tissues. This could potentially reduce the need for invasive surgeries.
Biofeedback Technology
Biofeedback technology is another emerging therapy. It helps patients control their physiological responses, like muscle tension, which can cause TMJ disorder. By managing these factors, patients can alleviate symptoms and enhance their quality of life.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements are also key in improving TMJ disorder diagnosis and treatment. Advanced imaging, like 3D cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), boosts diagnostic accuracy. Computer-aided design and manufacturing are used to create customized oral appliances and splints.
Multidisciplinary Approaches
TMJ disorder’s complexity demands a multidisciplinary treatment approach. This involves dental professionals, physical therapists, psychologists, and other specialists. This collaborative effort ensures all aspects of the disorder are addressed, leading to more effective care.
As research delves deeper into TMJ disorder, new treatments are expected to improve patient outcomes. Healthcare providers can offer the most effective and personalized care by staying updated with these advances.
Living Well with TMJ Disorder: Long-term Management Strategies
Managing Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMJ Disorder) demands a holistic approach. This includes making lifestyle changes, practicing self-care, and seeking professional advice. Understanding TMJ Disorder’s complexities and adopting long-term strategies can help alleviate symptoms. This, in turn, enhances one’s quality of life.
Living with TMJ Disorder means being aware of daily habits that can either worsen or improve symptoms. Stress management techniques, like meditation or deep breathing, can reduce stress’s impact on the TMJ. A balanced diet, avoiding extreme jaw movements, and gentle jaw exercises also play a role in long-term management.
Regular check-ins with healthcare professionals, including dentists and specialists, are vital. They help monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans as needed. Combining professional care with self-care practices enables individuals to manage TMJ Disorder effectively. This leads to active, fulfilling lives.
Managing TMJ Disorder is a continuous journey that requires patience, awareness, and a proactive mindset. By embracing these long-term strategies, individuals can significantly reduce TMJ Disorder’s impact on their daily lives. This improves their overall well-being while living with TMJ Disorder.
FAQ About Temporomandibular Joint Disorder
Q: What is Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMJ Disorder)?
A: TMJ Disorder impacts the jaw joint and surrounding muscles, leading to pain and discomfort. It can make everyday tasks like eating, speaking, and sleeping difficult.
Q: What are the common symptoms of TMJ Disorder?
A: Symptoms include jaw pain and tenderness, along with clicking, popping, or grating sounds when opening or closing the mouth. Limited jaw movement and referred pain patterns are also common. Some people may experience headaches, ear pain, or discomfort in the neck and shoulders.
Q: What causes TMJ Disorder?
A: TMJ Disorder can stem from physical trauma, bruxism (teeth grinding), stress, anxiety, arthritis, or dental issues like malocclusion.
Q: How is TMJ Disorder diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a physical exam, imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI, and TMJ assessments. A healthcare professional will assess symptoms and medical history to guide treatment.
Q: What are the treatment options for TMJ Disorder?
A: Treatment options include self-care, home remedies, medications, physical therapy, oral appliances, injections, and sometimes surgery.
Q: Can TMJ Disorder be managed without surgery?
A: Yes, many cases can be managed without surgery through self-care, lifestyle changes, and non-invasive treatments.
Q: How can I manage TMJ Disorder at home?
A: Home management includes jaw exercises, heat and cold therapy, dietary changes, stress management, and maintaining proper posture.
Q: What are the possible complications of untreated TMJ Disorder?
A: Untreated TMJ Disorder can cause chronic pain, impact daily activities, lead to psychological effects, result in joint damage, and disrupt sleep.
Q: When should I consult a healthcare professional for TMJ Disorder?
A: Seek professional help for persistent or severe symptoms, significant pain, limited jaw movement, or difficulty chewing.
Q: Are there any recent advances in TMJ Disorder treatment?
A: Yes, recent advances include regenerative medicine, biofeedback technology, and technological innovations in treatment approaches.
Q: How can I live well with TMJ Disorder?
A: Living well with TMJ Disorder involves adopting long-term management strategies, including self-care, lifestyle adjustments, and staying informed about new treatments and research.