What Are Toenail Tumors?
A toenail tumor is an abnormal growth that occurs under or around the toenail. It can be benign or malignant and may cause discomfort, pain, or changes in the appearance of the nail. The causes of such tumors can vary, including genetic predisposition, injury to the nail, or exposure to certain chemicals. Symptoms may include swelling, redness, or deformation of the nail. Treatment options depend on the nature of the tumor and can range from monitoring to surgical intervention.
Understanding the signs and seeking appropriate medical care is critical for effective management. Early diagnosis can significantly impact the outcome, making awareness of toenail health essential. Toenail tumors are a condition where abnormal cell growth happens near the toenail. These growths can be either benign or malignant. They may cause symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain.
Definition and Basic Characteristics
Toenail tumors are abnormal growths found under or around the toenail. They differ in appearance, growth rate, and whether they are benign or malignant. Knowing the basic characteristics of toenail tumors is key for diagnosis and treatment.
Prevalence and Demographics
Toenail tumors are less common than other types of tumors. Yet, some groups are more likely to develop these growths.
Age-Related Incidence
The occurrence of toenail tumors increases with age, mainly in those over 40. This age-related increase stresses the need for regular check-ups for early detection.
Gender Distribution
Research shows that toenail tumors can affect both genders, with a slight prevalence in women. The exact reasons for this gender distribution are unclear. Hormonal differences may play a role.
Types of Toenail Tumors
Toenail tumors fall into two main categories: benign and malignant. Each type has its own characteristics and implications for health. It’s essential to understand these differences for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Benign Toenail Tumors
Benign toenail tumors are non-cancerous growths. They don’t invade surrounding tissues or spread to other parts of the body. Despite being non-cancerous, they can cause discomfort and affect appearance.
Subungual Exostosis
Subungual exostosis is a benign tumor occurring under the toenail. It causes pain and nail deformity. Diagnosis often involves X-ray imaging.
Glomus Tumors
Glomus tumors are rare, benign growths from the glomus body under the nail. They cause severe pain, often triggered by temperature changes.
Onychomatricoma
Onychomatricoma is a rare, benign tumor of the nail matrix. It leads to thickening and discoloration of the nail plate. It’s often mistaken for a fungal infection.
Malignant Toenail Tumors
Malignant toenail tumors are cancerous. They can invade surrounding tissues and metastasize to other parts of the body. Early detection is critical for effective treatment.
Subungual Melanoma
Subungual melanoma is a skin cancer occurring under the nail. It’s challenging to diagnose and is often identified late, making it a serious condition.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is a malignant tumor that can occur under or around the toenail. It has the ability to invade deeper tissues if not treated promptly.
In conclusion, toenail tumors vary greatly in nature. From benign growths causing discomfort to malignant cancers needing immediate attention, accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management.
Common Causes of Toenail Tumor
Toenail tumors can stem from genetic, environmental, and health-related factors. Grasping these causes is vital for prevention and treatment.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predispositions significantly influence toenail tumor development. Those with a family history are more prone to these conditions. Both benign and malignant tumors can be affected by genetics.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors can also trigger toenail tumors. Trauma, UV radiation, and chemicals are known triggers. Reducing exposure to these can lower the risk.
Underlying Health Conditions
Underlying health conditions can raise the risk of toenail tumors. Autoimmune disorders and chronic infections hinder the body’s cell growth regulation.
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders, where the immune system attacks healthy cells, increase toenail tumor risk. Conditions like psoriasis and lupus cause inflammation and alter cell behavior.
Chronic Infections
Chronic infections, like those in the nail bed, can lead to toenail tumors. Fungal infections are common and can cause nail changes that may evolve into tumors.
Understanding these causes helps individuals take preventive measures. Early detection and intervention are essential for effective management.
Recognizing Toenail Tumor Symptoms
Identifying toenail tumor signs is vital for timely medical care. Toenail tumors can show up in different ways. It’s important to know the symptoms to get the right treatment.
Visual Changes to the Toenail
Visual signs are often the first clue to a toenail tumor. These signs can be color changes or structural alterations.
Color Abnormalities
Color changes under or around the toenail might signal a tumor. These can include:
- Dark streaks or spots
- Discoloration of the nail plate
- Changes in the nail’s natural color
Structural Changes
Structural changes also hint at a toenail tumor. Look out for:
- Thickening or distortion of the nail
- Lifting of the nail from the nail bed
- Fragmentation or brittleness of the nail
Pain and Discomfort Indicators
Pain and discomfort often accompany toenail tumors. The pain can vary from mild to severe. It might be constant or come and go.
Some signs include:
- Pain when pressure is applied to the toe
- Spontaneous pain without any apparent cause
- Discomfort when wearing shoes
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical help if you notice unusual toenail changes or persistent pain. Early detection is key to effective treatment.
If you see any symptoms, see a healthcare professional for an evaluation.
Diagnosing Toenail Tumors
Diagnosing toenail tumors requires a physical examination and advanced imaging tests. This method helps healthcare professionals accurately identify the tumor’s presence and type. A detailed diagnostic process is key to creating an effective treatment plan.
Initial Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing toenail tumors is a physical examination. A healthcare professional inspects the affected toenail and surrounding tissue for abnormalities. They look for signs like discoloration, thickening, or deformation. They also check for pain or tenderness.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are vital for a deeper evaluation of toenail tumors. These tests allow healthcare professionals to see the tumor and its impact on surrounding tissue.
X-rays
X-rays are used to examine the bone structure beneath the toenail. They help detect bone involvement or abnormalities. This is important for identifying conditions like subungual exostosis.
MRI Scans
MRI scans provide detailed images of soft tissue around the toenail. They help evaluate the tumor’s extent and its relation to nearby structures. MRI is essential for diagnosing soft tissue tumors.
Dermatoscopy
Dermatoscopy is a non-invasive technique that examines the skin and nail surface with a microscope. It helps identify toenail tumor characteristics, such as pigmentation patterns.
Biopsy Procedures
A biopsy involves removing tissue from the affected toenail for microscopic examination. It’s critical for determining the tumor’s type and malignancy.
Punch Biopsy
A punch biopsy removes a small, cylindrical tissue sample from the affected area. It’s useful for sampling small tumor areas.
Excisional Biopsy
An excisional biopsy surgically removes the entire tumor or a larger tissue sample. It’s used when a larger sample is needed for an accurate diagnosis.
Understanding Subungual Melanoma
Melanoma under the nail, known as subungual melanoma, is a serious health issue. It’s a skin cancer that can be hard to diagnose because its symptoms are not clear. This cancer can affect both fingernails and toenails, but it’s more common in toenails.
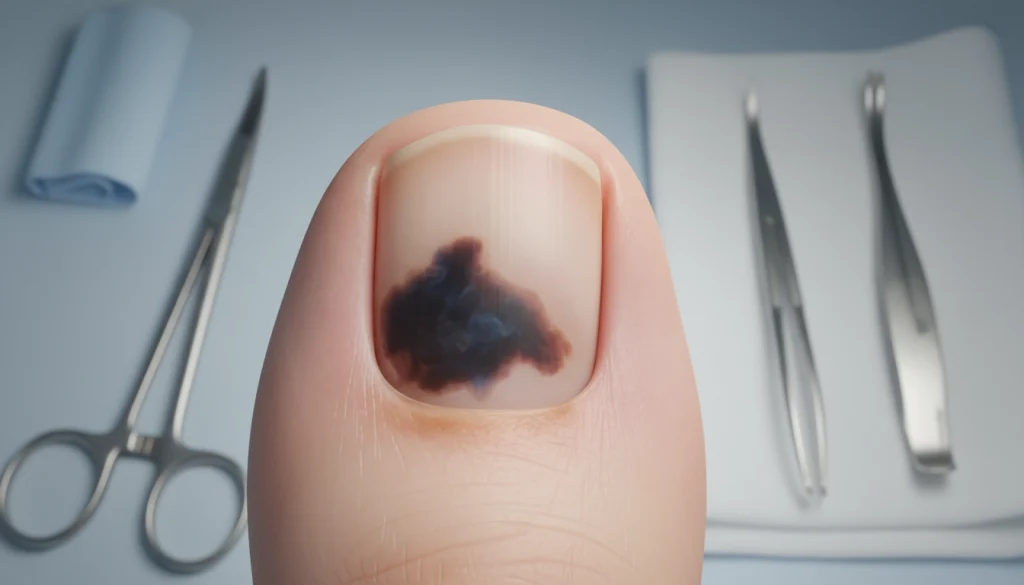
Signs and Symptoms
Spotting subungual melanoma early is key but tough. Common signs include a dark streak or spot under the nail, which can look like a bruise or fungal infection. Other symptoms might include nail changes, pain, or bleeding under the nail.
It’s important to watch for any changes in the nail’s look or feel. Catching it early can greatly improve treatment results.
Risk Factors
Several factors can raise the risk of getting subungual melanoma. These include genetic predisposition, nail trauma, and certain ethnic backgrounds. People with a family history of melanoma or previous skin cancers are at higher risk.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The outlook for subungual melanoma depends on when it’s caught. Early detection is key to better survival chances.
Early Detection Outcomes
When caught early, subungual melanoma has a much better five-year survival rate. Quick medical care can lead to more effective treatment and better results.
Advanced Stage Outcomes
On the other hand, advanced subungual melanoma has a worse prognosis with lower survival rates. Delayed diagnosis can lead to cancer spreading, making treatment harder.
Knowing the signs, symptoms, and risk factors of subungual melanoma is critical for early detection and effective treatment. Regular self-exams and quick medical visits for any suspicious changes can greatly improve outcomes.
Non-Melanoma Toenail Tumors
Non-melanoma toenail tumors encompass a wide range of lesions that can impact both the look and health of the toenail. These growths can stem from various tissues around the nail, resulting in distinct conditions.
Subungual Exostosis
Subungual exostosis is a benign bone tumor that develops under the nail. It manifests as a painful, hard growth, often causing the nail to detach from the nail bed. This condition frequently follows trauma to the toe.
Glomus Tumors
Glomus tumors are rare, benign growths that originate from the glomus body, a specialized structure involved in blood flow regulation. They are known for intense pain, exacerbated by temperature changes. These tumors are small and can be difficult to diagnose.
Onychomatricoma
Onychomatricoma is a rare, benign tumor of the nail matrix. It results in thickening of the nail plate, leading to pain and discomfort. This condition is often marked by a yellowish nail discoloration.
Grasping the nature of these non-melanoma toenail tumors is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Each condition presents unique characteristics, necessitating specific management strategies.
Treatment Options for Toenail Tumors
Managing toenail tumors requires a personalized approach. The treatment choice hinges on the tumor’s type, size, and severity, alongside the patient’s health status.
Surgical Approaches
Surgery is a common first step for toenail tumors. Various surgical methods exist, each suited for different scenarios.
Mohs Surgery
Mohs surgery is a detailed process. It removes the tumor in layers, checking each under a microscope until cancer-free. Ideal for tumors in delicate spots.
Wide Excision
Wide excision removes the tumor and some surrounding tissue. This ensures all cancer cells are removed, suitable for aggressive tumors.
Nail Matrix Excision
Nail matrix excision targets the area where nails grow. It’s used for tumors affecting this area.
Medication and Topical Treatments
For mild cases or those unsuitable for surgery, medication and topical treatments are suggested. These include creams or pills to shrink the tumor or alleviate symptoms.
Advanced Treatment for Malignant Cases
Malignant toenail tumors require more intense treatments. These aim to halt cancer spread and enhance survival chances.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy cancer cells. It’s often paired with other treatments for malignant toenail tumors.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy enhances the body’s immune response against cancer. It’s a hopeful option for some malignant toenail tumors.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Treatment
Recovery from toenail tumor treatment involves several steps, including rehabilitation and pain management. The aim is to restore normal foot function and reduce any discomfort or pain caused by the treatment.
Expected Recovery Timeline
The recovery time varies based on the treatment type. Minor procedures might allow patients to walk again in a few days. In contrast, more complex surgeries could need weeks for recovery. It’s vital to follow a post-operative care plan for proper healing.
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential. They help monitor the healing and address any issues promptly.
Physical Therapy Options
Physical therapy may be suggested to regain strength and mobility in the affected toe or foot. A physical therapist can create a tailored exercise program. This aims to enhance range of motion and decrease stiffness, which is key for those with extensive surgery.

Managing Pain and Discomfort
Effective pain management is a critical part of recovery. Patients might receive pain medication or be advised on over-the-counter options. Applying ice packs and elevating the foot can also help reduce swelling and pain.
It’s important for patients to discuss their pain levels with their healthcare provider. This ensures the treatment plan can be adjusted as needed.
Preventing Toenail Tumors
Preventing toenail tumors requires proactive steps and awareness of early signs. It’s about maintaining foot health and being mindful of lifestyle choices. This approach can significantly lower the risk of developing toenail tumors.
Proper Foot Hygiene
Good foot hygiene is key to preventing toenail tumors. It involves keeping feet clean and dry, trimming toenails straight, and avoiding shared personal care items.
- Wash your feet daily with soap and water.
- Dry your feet thoroughly, focusing on the areas between your toes.
- Trim toenails straight across to prevent ingrown toenails.
Regular Self-Examinations
Regular self-examinations are vital for early toenail tumor detection. It’s important to check your toenails for any color, shape, or texture changes.
- Watch for unusual toenail changes, like darkening or thickening.
- Be aware of any pain or tenderness around the toenail.
- Seek a healthcare professional’s advice if you spot any unusual changes.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes is essential in preventing toenail tumors. This includes protecting your feet from the sun and choosing the right footwear.
Sun Protection
It’s important to protect your feet from the sun. UV radiation can increase the risk of skin cancers, including those under the nail.
- Apply sunscreen to your feet when outdoors.
- Wear protective footwear or use umbrellas in direct sunlight.
Footwear Choices
Wearing the right shoes is critical in preventing toenail injuries and tumors. Opt for well-fitting shoes that don’t cause toe pressure or friction.
- Choose shoes with a wide toe box to reduce pressure.
- Avoid high heels or tight-fitting shoes.
Living With Toenail Tumor Conditions
Receiving a toenail tumor diagnosis can be overwhelming. Yet, with the right approach, managing this condition becomes more manageable. It’s not just about medical treatment; it’s also about adapting daily life.
Adapting Daily Activities
Adjusting daily routines is key in managing toenail tumors. This means wearing comfortable shoes and avoiding activities that stress the toes. These simple steps can greatly reduce discomfort.
Modifying your exercise routine is another effective strategy. For example, choosing low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can be beneficial. This approach helps maintain a good quality of life.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
The emotional toll of toenail tumors should not be overlooked. Anxiety, stress, and concerns about appearance or cancer risk can impact mental health. It’s vital to acknowledge these feelings and seek help.
Mental health professionals can offer valuable support. They provide coping strategies and help manage the emotional side of dealing with a toenail tumor.
Support Resources
Support resources are essential for coping with toenail tumors. They offer emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community.
Support Groups
Support groups, whether in-person or online, are invaluable. They provide a space to share experiences and learn from others. These groups offer emotional support and practical tips for managing the condition.
Online Communities
Online forums focused on toenail health or foot health are also beneficial. They allow individuals to ask questions, share their stories, and find support from those who understand their situation.
When to Get a Second Opinion
If you’ve been diagnosed with a toenail tumor, getting a second opinion can offer clarity and reassurance. It can confirm the initial diagnosis, provide more information about the tumor, and explore other treatment options.
Signs of Misdiagnosis
Misdiagnosis can happen if the first examination is not thorough or if symptoms resemble other conditions. Signs of a possible misdiagnosis include persistent pain, unusual nail changes, or no response to treatment.
- Unusual nail discoloration or thickening
- Persistent pain or discomfort
- Lack of improvement with standard treatments
Finding Specialized Care
For accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, it’s essential to consult specialists experienced in toenail tumors.
Dermatologists
Dermatologists specialize in skin conditions, including those affecting the nail and surrounding tissue. They can perform biopsies and guide on treatment options.
Podiatric Oncologists
Podiatric oncologists focus on cancers affecting the foot, including toenail tumors. They offer advanced treatments and surgical interventions. Seeking a second opinion from these specialists can greatly impact the management and outcome of toenail tumor treatment.
Advances in Toenail Tumor Research and Future Treatments
In recent years, toenail tumor research has made significant strides. This progress has shed new light on the causes and possible treatments for these conditions. Studies have delved into the genetic factors that lead to toenail tumors. They’ve also identified new targets for therapy.
Advanced imaging techniques are being explored for diagnosing and monitoring toenail tumors. Dermoscopy and confocal microscopy are showing promise. They could improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce the need for invasive procedures.
Research into the molecular mechanisms of toenail tumors is driving the development of new treatments. Emerging therapies, such as targeted treatments and immunotherapies, are showing great promise. They aim to enhance outcomes for patients with malignant toenail tumors.
As research continues, the management and treatment of toenail tumors are expected to improve. There will be a greater focus on personalized care and better patient outcomes. The integration of these advances into clinical practice will be key in shaping the future of toenail tumor treatment.
FAQ
Q: What is a toenail tumor?
A: A toenail tumor is an abnormal growth that can appear under, around, or on the toenail. It can be either benign or malignant.
Q: What are the common symptoms of a toenail tumor?
A: Common symptoms include visual changes to the toenail, such as color abnormalities or structural changes. Pain or discomfort is also common.
Q: How is a toenail tumor diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis starts with a physical examination. Imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans are then used. A biopsy is performed to determine the presence and type of tumor.
Q: What are the treatment options for toenail tumors?
A: Treatment options depend on the tumor’s type and severity. They may include surgical approaches, medication, topical treatments, or advanced treatments like chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Q: Can toenail tumors be prevented?
A: While not all toenail tumors can be prevented, proper foot hygiene and regular self-examinations are key. Lifestyle modifications, such as sun protection and careful footwear choices, can also help reduce risk.
Q: What is the recovery process like after treatment for a toenail tumor?
A: The recovery process varies based on the treatment. It includes a timeline that depends on the treatment type. Physical therapy options help regain mobility. Managing pain and discomfort during healing is also important.
Q: Are there support resources available for individuals with toenail tumors?
A: Yes, support resources like support groups and online communities are available. They help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological impact of toenail tumors.
Q: When should I seek a second opinion for a toenail tumor diagnosis?
A: Consider a second opinion if you notice signs of misdiagnosis or are unsure about the diagnosis or treatment plan. Look for specialized care from dermatologists or podiatric oncologists.