Trismus (Jaw Locking): What Is Trismus (Jaw Locking)?
Trismus, also known as jaw locking, is a condition where it’s hard to open the mouth. It can greatly affect daily life, making eating, speaking, and oral health challenging. This condition impacts an individual’s quality of life significantly. Causes of trismus include trauma, temporomandibular joint disorders, infections, or tumors. Symptoms include pain, stiffness, and trouble opening the mouth. It’s important to understand these causes and symptoms to choose the right treatment.
Treatment for trismus varies. It can range from simple management techniques to more complex procedures. The choice depends on the condition’s severity and cause. Trismus, or jaw locking, is a condition that limits jaw movement. It causes discomfort and makes everyday tasks like eating and speaking hard. This condition restricts the jaw’s normal function.
Definition and Medical Classification
Trismus is a condition where jaw opening is reduced. This happens due to muscle spasms or inflammation. It falls under different medical categories based on its cause.
Knowing the type of trismus is vital for treatment. It helps determine if the condition is acute or chronic. Identifying the cause is also key to managing it well.
Normal Jaw Function vs. Restricted Movement
Normal jaw function allows for smooth TMJ and muscle movement. This enables various jaw motions like opening, closing, and side-to-side movements. Trismus, on the other hand, restricts these movements.
This restriction makes eating, speaking, and oral hygiene challenging. It significantly affects daily life. Understanding the difference between normal jaw function and trismus is critical for diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Jaw Anatomy and Function
Comprehending the jaw’s anatomy and function is key to grasping trismus. The mandible, or jaw, is intricately designed. It’s essential for everyday tasks like eating, speaking, and showing emotions.
Temporomandibular Joint Structure
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) links the mandible to the skull’s temporal bone. It’s a complex hinge joint, enabling a variety of movements.
The TMJ includes the articular eminence, mandibular condyle, and articular disc. The disc is vital, dividing the joint into two parts for smooth movement.
Muscles Involved in Jaw Movement
A group of muscles coordinate to control jaw movement. They manage opening, closing, and side-to-side jaw actions.
Masseter and Temporalis Muscles
The masseter muscle is key in closing the jaw. It’s a thick, fan-shaped muscle connecting the zygomatic arch to the mandible.
The temporalis muscle, a broad, flat muscle on the temporal bone, elevates the mandible to close the jaw.
Pterygoid Muscles and Supporting Structures
The pterygoid muscles, including the lateral and medial pterygoids, are vital for jaw movement. The lateral pterygoid helps open the jaw and protrude the mandible. The medial pterygoid aids in jaw elevation.
Ligaments and the articular disc provide stability to the TMJ. They ensure smooth, coordinated movements.
Types and Classifications of Trismus
Grasping the different types of trismus is key to accurate diagnosis and treatment. This jaw locking condition can vary in severity and impact, affecting patients’ lives significantly.
Acute vs. Chronic Trismus
Trismus is divided into acute and chronic forms based on its duration. Acute trismus occurs suddenly, often due to recent trauma, surgery, or infection. On the other hand, chronic trismus lasts longer and may stem from ongoing or recurring issues.
- Acute trismus: Sudden onset, often related to recent trauma or surgery.
- Chronic trismus: Long-term condition, potentially resulting from prolonged inflammation or other persistent factors.
Severity Scales and Measurement
Measuring trismus severity involves several scales and methods. These provide a clear understanding of the condition’s impact. Key among these are Maximum Interincisal Opening (MIO) measurements and Functional Impact Classification.
Maximum Interincisal Opening (MIO) Measurements
MIO gauges the gap between the upper and lower incisors at maximum opening. It directly reflects jaw mobility. Lower MIO values signify more severe trismus.
Functional Impact Classification
This classification evaluates how trismus affects daily activities like eating, speaking, and oral hygiene. It offers insights into the condition’s practical effects on a patient’s life.
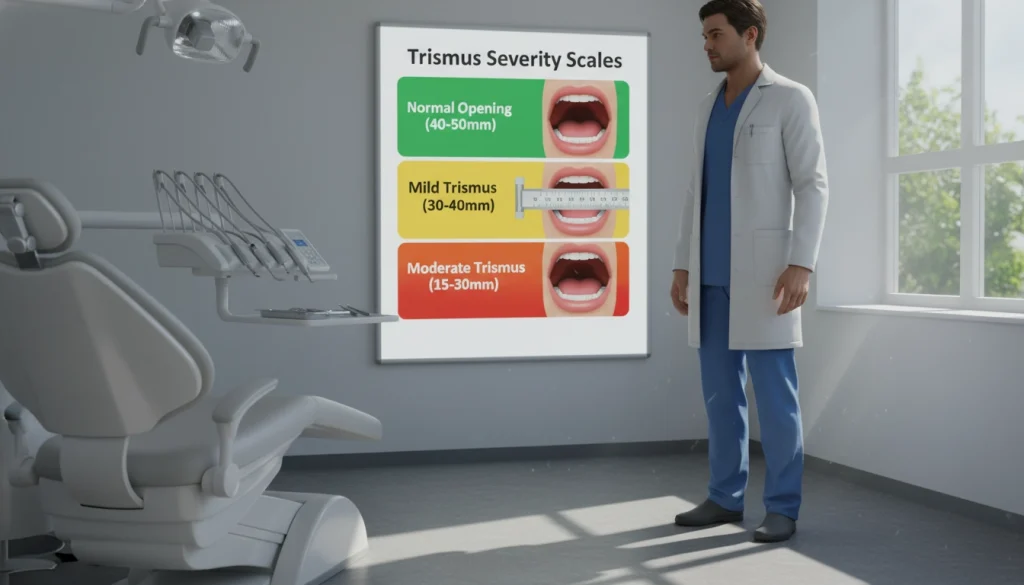
Healthcare professionals can improve diagnosis and management of trismus by understanding these classifications and measurement techniques. This allows for tailored treatments that meet each patient’s unique needs.
Trismus (Jaw Locking): Common Causes and Triggers
Understanding the causes of trismus is vital, as it can arise from several sources. These include surgical procedures, physical trauma, and inflammatory conditions. Trismus, or jaw locking, severely impacts an individual’s quality of life by restricting jaw movement.
Dental and Oral Surgery Complications
Dental and oral surgery are leading causes of trismus. Complications from these procedures can cause inflammation and pain, limiting jaw mobility. For example, wisdom teeth extraction often results in trismus due to trauma to surrounding tissues.
TMJ Disorders and Dysfunction
TMJ disorders are a significant cause of trismus. The TMJ connects the jawbone to the skull, and dysfunction here restricts jaw movement. Conditions like TMJ arthritis or disc displacement can trigger trismus.
Trauma and Physical Injury
Trauma to the jaw or face can induce trismus by causing pain and inflammation. Physical injuries, whether from sports, accidents, or physical altercations, can directly affect the jaw’s range of motion.
Infection and Inflammatory Conditions
Infections and inflammatory conditions, such as tetanus or oral cavity infections, can also cause trismus. These conditions lead to muscle spasms and pain, restricting jaw movement.
In conclusion, trismus is a complex condition with various causes. These include surgical complications, TMJ disorders, trauma, and infections. Understanding these causes is key to effective management and treatment.
Risk Factors for Developing Trismus
Understanding the risk factors for trismus is key to early detection and prevention. Trismus can arise from a mix of factors. It’s vital to pinpoint those at higher risk.
Demographic and Genetic Predispositions
Certain demographic traits and genetic predispositions heighten the risk of trismus. For example:
- Age: Older adults face a higher risk due to reduced jaw mobility and increased dental issues.
- Genetic predisposition: Those with a family history of TMJ disorders or jaw issues are more at risk.
- Previous medical conditions: Conditions like oral submucous fibrosis can raise the risk of trismus.
Lifestyle and Environmental Contributors
Lifestyle and environmental factors significantly influence trismus development. Key contributors include:
- Poor oral hygiene and dental care, leading to infections and inflammation.
- Trauma or injury to the jaw, face, or head, causing trismus.
- Radiation therapy to the head and neck, potentially causing fibrosis and restricted jaw movement.
Healthcare professionals can develop targeted prevention strategies. They can also offer early intervention for those at high risk of trismus.
Recognizing Trismus Symptoms
Identifying trismus symptoms early is key to timely diagnosis and treatment. Trismus, or jaw locking, presents through various physical and secondary symptoms. These symptoms can greatly affect an individual’s quality of life.
Primary Physical Manifestations
The primary signs of trismus include limited jaw mobility and pain. These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities.
Limited Mouth Opening
Limited mouth opening is a key symptom of trismus. People may struggle to open their mouths fully. This can make eating, speaking, and oral hygiene challenging.
Pain and Discomfort Patterns
Pain from trismus can vary from mild to severe and is often in the jaw area. Discomfort patterns differ, with some experiencing constant pain. Others may have pain triggered by actions like chewing.
Secondary Symptoms and Warning Signs
There are secondary symptoms and warning signs that may indicate trismus. These include:
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Jaw stiffness or clicking sounds
- Headaches or earaches due to referred pain
- Changes in bite alignment or tooth wear
Recognizing these secondary symptoms is essential for a complete diagnosis and treatment plan.

Diagnostic Process for Trismus
To accurately diagnose trismus, healthcare providers employ a variety of clinical examination techniques and imaging studies. The diagnostic process is vital for understanding the severity and cause of trismus. This understanding guides the treatment plan.
Clinical Examination Techniques
Clinical examination techniques are key in diagnosing trismus. Healthcare professionals assess the patient’s ability to open their mouth. They check for any limitations in jaw movement and evaluate pain or discomfort during jaw movement.
- Measuring the maximum inter-incisal distance
- Assessing the range of motion of the temporomandibular joint
- Palpating the muscles of mastication for tenderness
Imaging Studies and Tests
Imaging studies are critical in diagnosing trismus by providing detailed images of the jaw and surrounding structures. These images help identify any abnormalities causing the condition.
X-rays and CT Scans
X-rays evaluate the bone structure of the jaw, while CT scans offer more detailed cross-sectional images. These imaging modalities help detect fractures, bone spurs, or other bony abnormalities.
MRI and Specialized Imaging
MRI is useful for assessing soft tissue abnormalities, such as inflammation or tumors, that may cause trismus. Specialized imaging techniques may also be used to evaluate the temporomandibular joint in detail.
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
When diagnosing trismus, it’s essential to consider other conditions that may present with similar symptoms. Differential diagnosis involves ruling out other causes of jaw restriction or pain. This includes temporomandibular joint disorders, infections, or malignancies.
Potential Complications of Untreated Trismus
Trismus left untreated can significantly impact an individual’s life quality. It can lead to both short-term functional issues and long-term health problems.
Short-term Functional Impacts
Trismus can hinder daily activities in the short term. It affects nutrition and communication.
Nutritional Challenges
Difficulty in chewing and swallowing can result in nutritional deficiencies. This includes:
- Challenges in consuming solid foods
- Avoidance of certain foods due to pain
- Risk of malnutrition from inadequate nutrient intake
Speech and Communication Issues
Restricted jaw movement impacts speech, causing communication difficulties. These issues include:
- Articulation problems due to limited mouth opening
- Changes in speech clarity
- Potential for social isolation due to communication barriers
Long-term Health Consequences
Untreated trismus can lead to severe, long-lasting health issues. These may include:
- Chronic pain conditions
- Persistent nutritional deficiencies
- Potential for further dental or oral health problems
Recognizing these complications emphasizes the need for medical attention for trismus. Early treatment can prevent both short-term and long-term issues, improving life quality.
Medical Treatment Approaches
Trismus treatment involves various strategies to alleviate symptoms and restore jaw function. Each treatment plan is customized based on the underlying cause, severity, and its impact on the patient’s quality of life.
Pharmacological Interventions
Pharmacological interventions are key in managing trismus symptoms. They aim to reduce pain, inflammation, and muscle spasms.
Anti-inflammatory Medications
Anti-inflammatory medications, such as NSAIDs, are commonly used to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with trismus. These medications are effective in cases where inflammation plays a role.
Muscle Relaxants and Pain Management
Muscle relaxants are prescribed to manage muscle spasms and tension. Additional pain management strategies may be employed for severe pain.
Surgical and Invasive Procedures
In cases of anatomical issues or severe trauma, surgical or invasive procedures may be necessary. These can include interventions to release scar tissue, repair or replace the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), or other corrective surgeries.
Emerging Treatment Modalities
Research into trismus treatment continues to evolve, with emerging modalities promising new hope for patients. These include innovative pharmacological agents, advanced surgical techniques, and alternative therapies such as botulinum toxin injections.
Understanding the range of medical treatment approaches available helps healthcare providers develop effective treatment plans tailored to individual patients with trismus.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Techniques
For those dealing with trismus, physical therapy and rehabilitation can greatly help. These methods aim to ease symptoms and boost life quality. Physical therapy plays a key role in treating trismus, aiming to restore jaw function and lessen pain.
Therapeutic Jaw Exercises
At the heart of physical therapy for trismus are therapeutic jaw exercises. These exercises aim to boost jaw mobility, strengthen jaw muscles, and improve oral function.
Passive Stretching Techniques
Passive stretching techniques use external forces to stretch the jaw. This is done through manual therapy by a physical therapist or specialized devices. The goal is to increase jaw mobility without causing pain.
Active Range-of-Motion Exercises
Active range-of-motion exercises require patients to move their jaw actively. This includes opening and closing the mouth or moving it from side to side. These exercises help maintain and enhance jaw mobility, guided by a physical therapist.
Professional Therapy Approaches
Professional therapy for trismus employs various techniques. Physical therapists use manual therapy, like massage and mobilization, to reduce muscle tension and enhance jaw function. Modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation are also used to aid healing and muscle relaxation.
A thorough physical therapy program for trismus may also include education on jaw mechanics and posture correction. It teaches strategies for managing pain and discomfort. This approach significantly improves a patient’s ability to perform daily tasks and enhances their overall quality of life.
- Physical therapy helps improve jaw mobility.
- Therapeutic exercises strengthen jaw muscles.
- Professional therapy approaches include manual therapy and modalities.
Home Remedies and Self-Care Strategies
Medical treatments are not the only solution for trismus symptoms. Home remedies and self-care strategies can also offer relief. These methods can enhance comfort and improve jaw mobility.
Heat and Cold Therapy Applications
Applying heat or cold to the affected area can provide relief. Heat therapy, such as using a warm compress, can relax the jaw muscles. Cold therapy can reduce inflammation and numb the pain.
- Use a warm washcloth or a heating pad on a low setting.
- Apply an ice pack wrapped in a cloth to avoid direct contact with the skin.
- Alternate between heat and cold therapy to find what works best.
Dietary Modifications for Comfort
Dietary changes can significantly impact trismus management. Consuming soft foods and avoiding hard or chewy items can reduce strain on the jaw.
- Eat soft, bland foods like yogurt, scrambled eggs, and mashed potatoes.
- Avoid foods that require extensive chewing, such as nuts, raw vegetables, and tough meats.
- Opt for liquid or pureed meals if chewing is extremely painful.
Stress Management and Relaxation Techniques
Stress can exacerbate trismus symptoms. Practicing relaxation techniques can help manage stress and reduce jaw tension.
- Engage in meditation or deep breathing exercises.
- Practice gentle jaw stretches and relaxation exercises.
- Consider progressive muscle relaxation to release overall tension.
By incorporating these home remedies and self-care strategies, individuals with trismus can better manage their symptoms. This can significantly improve their quality of life.
Preventing Trismus Recurrence
Preventing trismus recurrence requires a blend of exercises, lifestyle changes, and medical treatments. Understanding the causes of trismus is key. Taking proactive steps can greatly lower the risk of its return.
Maintenance Exercises and Routines
Regular exercises are vital for keeping the jaw mobile and preventing trismus. Simple jaw exercises, like opening and closing the mouth, and lateral movements, should be done daily. 
- Perform jaw opening exercises with a finger or device to gradually increase mouth opening.
- Engage in lateral movements to enhance jaw mobility.
- Practice relaxation techniques to reduce muscle tension.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Preventive Measures
Making lifestyle changes is also essential in preventing trismus recurrence. This includes dietary adjustments, avoiding extreme jaw movements, and stress management. Eating soft foods and avoiding hard or chewy foods can lessen jaw strain.
- Avoid foods that require wide mouth opening or heavy chewing.
- Practice stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to reduce overall muscle tension.
- Regularly check and adjust your posture to avoid putting unnecessary strain on your jaw.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s vital to recognize the signs that indicate the need for medical attention for effective trismus management. Trismus, or jaw locking, can be a symptom of an underlying condition that requires prompt medical evaluation.
Emergency Warning Signs
Certain symptoms require immediate medical attention. These include severe jaw pain, difficulty breathing, or an inability to open the mouth. If you experience any of these emergency warning signs, seek help immediately.
- Severe jaw pain or locking
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Fever or signs of infection
Finding the Right Healthcare Specialist
For proper diagnosis and treatment, it’s essential to consult the right healthcare specialist. Depending on the cause and severity of trismus, different specialists may be involved.
Dentists and Oral Surgeons
Dentists and oral surgeons play a critical role in diagnosing and treating trismus related to dental or oral surgery complications. They can provide guidance on managing symptoms and addressing underlying causes.
Physical Therapists and Pain Specialists
Physical therapists can help with exercises and stretches to improve jaw mobility. Pain specialists can offer treatments to manage chronic pain associated with trismus.
Living with Chronic Trismus
Dealing with chronic trismus is more than just managing a medical issue; it’s about adapting to a new reality. This condition, marked by persistent jaw locking or restriction, profoundly impacts daily life. It affects everything from eating and speaking to overall comfort and well-being.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
The psychological and emotional effects of chronic trismus are significant. People may feel frustrated, anxious, and depressed due to the condition’s chronic nature. Simple tasks become daunting, leading to feelings of isolation and dependency on others.
The emotional burden is as severe as the physical symptoms. It’s essential to address both aspects in managing chronic trismus.
Support Resources and Patient Communities
Fortunately, those with chronic trismus are not isolated. Support resources and patient communities offer help, understanding, and guidance. These include online forums, support groups, and professional counseling services designed for chronic condition sufferers.
Connecting with these resources provides emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community. It helps individuals manage the challenges of chronic trismus more effectively.
Moving Forward: Advancements in Trismus Treatment
Research into trismus, or jaw locking, is revealing new insights. This has led to the development of innovative treatments. These advancements are set to improve patient outcomes and enhance quality of life.
Future treatments for trismus will likely combine pharmacological, physical, and regenerative therapies. Scientists are looking into novel medications and injection therapies to ease symptoms and boost jaw mobility.
Physical therapy methods are also evolving. There’s a focus on personalized exercise programs and manual therapies. Technologies like ultrasound and laser therapy may also play a role in improving treatment results.
As the field advances, patients with trismus can look forward to more effective treatments. This will lead to better management of the condition and improved overall well-being.
FAQ
Q: What is trismus, and how is it different from a normal jaw function?
A: Trismus, also known as jaw locking, is a condition where the jaw’s range of motion is reduced. This makes it hard to open or close the mouth. Unlike normal jaw function, trismus involves restricted movement, often accompanied by pain or discomfort.
Q: What are the common causes of trismus?
A: Trismus can result from various factors, including dental and oral surgery complications, TMJ disorders, trauma, infection, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding the underlying cause is key for effective treatment.
Q: How is trismus diagnosed?
A: Diagnosing trismus involves a clinical examination, imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI, and sometimes specialized tests. Healthcare professionals assess the severity and underlying cause to develop a treatment plan.
Q: What are the treatment options for trismus?
A: Treatment approaches for trismus include pharmacological interventions like anti-inflammatory medications and muscle relaxants, surgical and invasive procedures, physical therapy, and rehabilitation techniques. Emerging treatment modalities are also being explored.
Q: Can trismus be prevented, and how can recurrence be avoided?
A: Preventing trismus involves avoiding risk factors, maintaining good oral health, and managing conditions like TMJ disorders. To prevent recurrence, patients can perform maintenance exercises, make lifestyle adjustments, and follow preventive measures.
Q: What are the potentially complications of untreated trismus?
A: Untreated trismus can lead to short-term functional impacts like nutritional challenges and speech issues, as well as long-term health consequences. Seeking timely medical attention is essential to avoid these complications.
Q: How can physical therapy help in managing trismus?
A: Physical therapy plays a critical role in treating trismus through therapeutic jaw exercises, passive stretching, and active range-of-motion exercises. Professional therapy approaches can also help improve jaw mobility and reduce pain.
Q: What self-care strategies can help manage trismus symptoms?
A: Home remedies and self-care strategies, including heat and cold therapy, dietary modifications, and stress management techniques, can complement medical treatments and help alleviate trismus symptoms.
Q: When should I seek medical attention for trismus?
A: It’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience emergency warning signs or persistent symptoms of trismus. Consulting the right healthcare specialist, such as a dentist, oral surgeon, or physical therapist, can ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.