Uterine Cancer: What is Uterine Cancer?
Uterine cancer is a serious health issue for women, mainly in the United States. It’s important to grasp the basics of this condition. This understanding highlights its impact and the need for early detection. The uterus is essential in the female reproductive system. Cancer here can have severe consequences. Knowing the signs and risk factors helps in early medical intervention. This can significantly improve outcomes for those affected.
Exploring uterine cancer reveals the critical role of awareness and education. These elements are vital in the battle against this disease. Understanding uterine cancer requires knowledge of the uterus and its role in women’s health. Uterine cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the uterus. This is a critical part of the female reproductive system.
Definition and Basic Anatomy
The uterus is a hollow, muscular organ where a fetus grows during pregnancy. Uterine cancer begins when abnormal cells in the uterus grow and multiply uncontrollably. The most common type of uterine cancer is endometrial cancer, which starts in the lining of the uterus (endometrium).
Understanding the uterine anatomy is key to grasping how uterine cancer develops.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of uterine cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes. Recognizing the signs and symptoms early can lead to timely medical intervention. Common symptoms include abnormal vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain.
Knowing the risk factors and symptoms can aid in early detection and effective management of uterine cancer.
Types of Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer encompasses various forms, including endometrial cancer and uterine sarcoma. Each type requires specific diagnosis and treatment approaches. Understanding these differences is vital for effective care.
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer begins in the uterus’s lining, known as the endometrium. It’s the most prevalent form, making up the bulk of cases. Uterine sarcoma, by contrast, is a rare cancer that starts in the uterine wall’s muscle or other tissues. Symptoms like abnormal vaginal bleeding often lead to early detection of endometrial cancer.
Factors increasing the risk of endometrial cancer include obesity, hormonal imbalances, and genetic syndromes. Treatment usually involves surgery, with radiation or chemotherapy added based on the cancer’s stage and grade.
Uterine Sarcoma
Uterine sarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer type. It originates from the uterus’s muscle layer or supporting tissues. Like endometrial cancer, it can cause abnormal vaginal bleeding. Yet, uterine sarcoma grows and spreads more rapidly.
Diagnosis of uterine sarcoma typically involves a biopsy or surgery. Treatment may include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, depending on the cancer’s stage and type. Due to its rarity, specialized cancer centers often handle its treatment.
Epidemiology of Uterine Cancer
Understanding uterine cancer’s epidemiology is key to identifying risk factors and developing targeted interventions. This involves analyzing prevalence, incidence, and demographic characteristics. Such analysis informs public health strategies and clinical practices.
Prevalence in the United States
In the United States, uterine cancer is a major health concern, significantly impacting women’s health. Recent data show it’s the most common gynecologic malignancy in American women. Factors like age, obesity, and hormonal influences affect its prevalence in the U.S.
The American Cancer Society projects a substantial number of new uterine cancer cases in the U.S. annually. This underlines the necessity for ongoing research and awareness.
Global Statistics
Globally, uterine cancer is a significant health issue, with varying incidence rates across regions and populations. It’s more prevalent in developed countries, where lifestyle and environmental factors may play a role.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer offers valuable data on uterine cancer’s global burden. This data helps identify trends and patterns, guiding international health initiatives.
Understanding the Female Reproductive System
Grasping the complexities of the female reproductive system is key to understanding uterine cancer’s development and progression. This system is a complex network of organs, each playing a critical role in reproductive health.
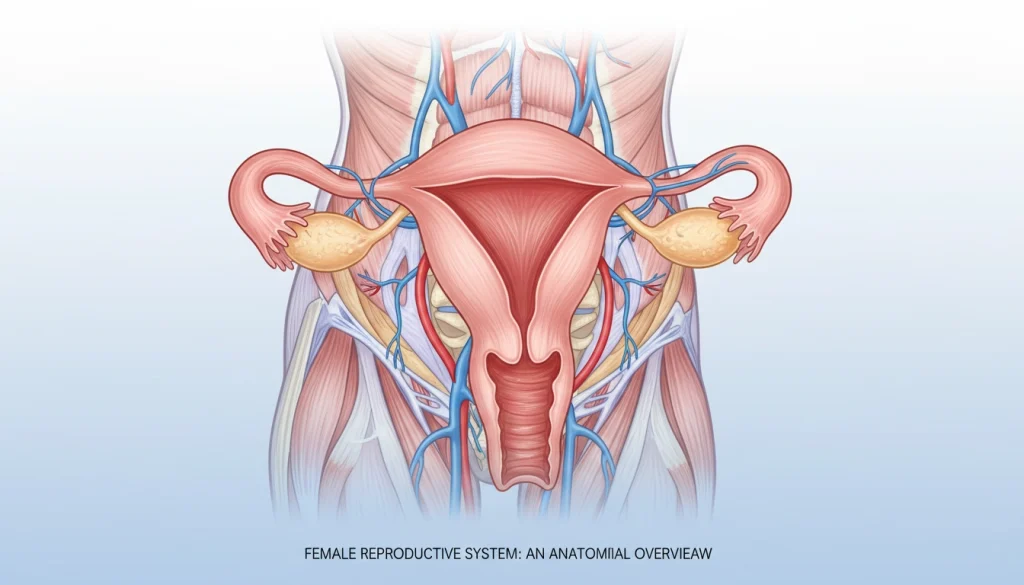
Uterine Structure and Function
The uterus is a vital, hollow organ essential for fetal development during pregnancy. It consists of:
- The endometrium, the inner lining that thickens and sheds with each menstrual cycle.
- The myometrium, a thick layer of smooth muscle that contracts during childbirth.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones have a profound impact on the female reproductive system. Estrogen and progesterone are central to regulating:
- The menstrual cycle, through the thickening and shedding of the endometrium.
- Reproductive processes, including pregnancy and childbirth.
Any imbalance in these hormones can lead to reproductive health issues. This includes an elevated risk of uterine cancer.
Risk Factors for Uterine Cancer
The risk of uterine cancer is shaped by several factors, including age, hormonal influences, and specific medical conditions. Recognizing these risks is vital for prevention and early detection.
Age and Hormonal Factors
Age is a major risk factor, with most cases occurring in women post-menopause, between 55 and 65. Hormonal factors, such as estrogen exposure, also play a significant role. Women with early menstruation or late menopause face higher risks due to prolonged estrogen exposure.
Hormonal imbalances, like those in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can also increase risk. The use of estrogen-alone hormone replacement therapy (HRT) during menopause further raises the risk of uterine cancer.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can elevate the risk of uterine cancer. Obesity, linked to higher estrogen levels, and diabetes are among these. Women with Lynch syndrome, a genetic disorder, are also at increased risk.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle and environmental factors also impact uterine cancer risk. A diet rich in saturated fats and low in fruits and vegetables can increase risk. Lack of physical activity and being overweight or obese also contribute to higher risk.
Understanding these risk factors is essential for early detection and prevention of uterine cancer. While some risks are unavoidable, being aware of them allows for monitoring and potentially reducing risk through lifestyle changes and medical interventions.
Signs and Symptoms of Uterine Cancer
Identifying the signs and symptoms of uterine cancer is critical for women’s health. It enables timely medical intervention. Uterine cancer can show through various symptoms. Being aware of these can greatly influence treatment outcomes.
Early Warning Signs
Early signs of uterine cancer often include abnormal vaginal bleeding. This can be a change in menstrual patterns or bleeding after menopause. Other symptoms may involve pelvic pain or discomfort and unusual vaginal discharge. These signs can be subtle, and some women may not seek medical attention immediately. It’s vital to be vigilant about any changes in bodily functions.
Advanced Symptoms
As uterine cancer progresses, symptoms can worsen. They may include significant weight loss, fatigue, and pain in the pelvic area or lower back. Advanced uterine cancer might also cause swelling in the legs due to blood flow blockage. Recognizing these advanced symptoms is critical for adjusting treatment plans.
Women should be aware of their bodies and report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider. Early detection and understanding of uterine cancer signs and symptoms can significantly improve treatment efficacy.
When to See a Doctor
Knowing when to seek medical help is key for catching uterine cancer early. It’s vital to recognize the signs and symptoms that call for a doctor’s visit. This can greatly affect your health.
Concerning Symptoms That Require Medical Attention
Abnormal vaginal bleeding is a red flag. This includes bleeding between periods, heavy or prolonged menstrual flow, or postmenopausal bleeding. Also, pelvic pain or pressure and unexplained weight loss are symptoms that need immediate attention.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Unexplained weight loss
Preparing for Your Appointment
Before your doctor’s visit, compile a list of your symptoms. Include when they started and how often they happen. Also, mention any medical conditions, medications, and family cancer history.
Being well-prepared helps your doctor understand your situation. This leads to more effective care.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing uterine cancer involves a mix of physical exams, imaging tests, and lab analyses. These steps are vital for pinpointing uterine cancer and tailoring the right treatment.
Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing uterine cancer is a physical exam. A healthcare provider may conduct a pelvic exam. This checks for any irregularities in the uterus, like unusual bleeding or an enlarged uterus.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests help see the uterus and surrounding areas. Common ones include ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans. These tools help spot tumors and gauge their size and location.
Biopsy Procedures
A biopsy takes a tissue sample from the uterus for microscopic examination. There are various biopsy methods, like endometrial biopsy and dilation and curettage (D&C). The sample is checked for cancer cells.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests analyze tissue samples from biopsies. These include histopathology to study tissue structure and detect cancer cells. These tests are key to confirming uterine cancer diagnosis.
Staging and Grading of Uterine Cancer
Staging and grading of uterine cancer are key in determining treatment options and predicting outcomes. They help healthcare providers grasp the disease’s extent. This knowledge is essential for crafting an effective treatment plan.
The FIGO Staging System
The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) staging system is a cornerstone in classifying uterine cancer. It categorizes the cancer based on tumor size, invasion depth, and spread to nearby or distant tissues.
The FIGO staging system encompasses several stages:
- Stage I: Cancer is confined to the uterus.
- Stage II: Cancer has spread to the cervix.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs or tissues.
Understanding Cancer Grades
Cancer grading examines cancer cells under a microscope. It reveals how much these cells resemble normal cells. This information is vital in assessing the cancer’s aggressiveness.
There are three primary grades:
- Grade 1: Well-differentiated cells that closely resemble normal cells.
- Grade 2: Moderately differentiated cells that are somewhat abnormal.
- Grade 3: Poorly differentiated cells that are very abnormal.
Knowing the grade of uterine cancer aids in planning the most suitable treatment. It helps in tailoring the approach to the disease’s aggressiveness.
Treatment Options for Uterine Cancer
Understanding the various treatment options is key to effectively managing uterine cancer. The choice of treatment hinges on several factors. These include the cancer’s type and stage, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is a primary treatment for uterine cancer. It often involves a hysterectomy, which removes the uterus. In some cases, the surgeon may also remove the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus.
- Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy: Removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- Lymphadenectomy: Removal of lymph nodes to check for cancer spread.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy employs high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with surgery.
- External beam radiation therapy: Targets cancer cells from outside the body.
- Internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy): Places radioactive material inside the body near the cancer.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It is often used for advanced uterine cancer or when the cancer has spread.
- Systemic chemotherapy: Drugs are given orally or intravenously to target cancer cells throughout the body.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is used to treat cancers that are hormone-sensitive. It works by blocking the body’s natural hormones.
- Progestins: Synthetic versions of progesterone, used to slow the growth of hormone-sensitive tumors.
- Tamoxifen: Can be used in some cases, though it’s more commonly associated with breast cancer treatment.
Treatment plans are highly individualized. Patients should discuss their options with their healthcare provider. This helps determine the best course of action.
Managing Treatment Side Effects
Managing the side effects of uterine cancer treatment is vital for maintaining the patient’s quality of life. Treatments like surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or hormone therapy can cause various side effects. These can significantly impact a patient’s well-being.
Common Side Effects and Their Management
Common side effects include fatigue, nausea, and changes in bowel habits. Managing these often requires a mix of medical treatments and lifestyle changes. For example, anti-nausea medication can reduce nausea, while dietary adjustments can help with bowel issues.
Patients are encouraged to lead a healthy lifestyle. This includes a balanced diet and regular exercise to lessen side effects. Counseling or joining support groups can also offer emotional support during this difficult time.
Long-term Considerations
Long-term, patients should watch for late effects of treatment, such as secondary cancers or organ issues. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are key for early detection and management. This helps prevent or mitigate these complications.
Patients may also need to make lasting lifestyle changes to cope with treatment’s physical and emotional impacts. This could involve ongoing psychological support and adapting daily routines to manage treatment’s lasting effects.
Advanced and Recurrent Uterine Cancer
Diagnosing advanced or recurrent uterine cancer demands a detailed approach. This is due to the complexities and challenges these stages present.
Treatment Approaches for Advanced Disease
Advanced uterine cancer calls for aggressive, often multi-faceted treatments. These may include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy. Each is chosen based on the patient’s condition and the cancer’s specifics.
- Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible
- Radiation therapy to target remaining cancer cells
- Chemotherapy to address any systemic spread
- Hormone therapy for cancers that are hormone-receptor-positive

Managing Recurrence
Managing recurrent uterine cancer requires a thorough review of past treatments and the current disease extent. Treatment options may include reoperation, additional radiation, or systemic therapies like chemotherapy or hormone therapy.
It’s essential for patients with recurrent uterine cancer to be managed by a multidisciplinary team. This approach optimizes care and improves outcomes.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Prognosis and survival rates for uterine cancer vary significantly based on the stage at diagnosis and other individual factors. Understanding these elements is critical for both patients and healthcare providers. It helps in making informed decisions about treatment and care.
Factors Affecting Prognosis
Several factors influence the prognosis of uterine cancer. These include the stage of cancer at diagnosis, the type and grade of the tumor, the patient’s overall health, and how well the cancer responds to treatment.
- The stage at which uterine cancer is diagnosed plays a critical role in determining prognosis.
- The type and grade of the tumor also significantly affect the outlook for patients.
- Patient’s overall health and presence of other medical conditions can influence treatment options and outcomes.
Five-Year Survival Statistics
Five-year survival rates are commonly used to provide a general outlook for patients with uterine cancer. According to recent data, the overall five-year survival rate for uterine cancer is promising. This is true, even more so when diagnosed at an early stage.
For patients diagnosed with localized uterine cancer, the five-year survival rate is significantly higher. This is compared to those diagnosed with cancer that has spread to distant parts of the body.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While not all uterine cancer cases can be prevented, certain steps can lower the risk. It’s vital for women, and those at higher risk, to understand these preventive strategies. This knowledge is key to maintaining women’s health.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle choices are critical in reducing uterine cancer risk. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as obesity is a known risk factor. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with regular exercise, aids in weight management and overall health. These habits can significantly reduce the risk.
Managing conditions like diabetes and hypertension is also important. These conditions increase the risk of uterine cancer. Lifestyle changes and medical treatment can help manage them effectively.
Regular Screenings and Check-ups
Regular health check-ups and screenings are essential for early detection and prevention. There’s no specific screening test for uterine cancer like there is for cervical cancer. Yet, regular pelvic exams and discussing risk factors with a healthcare provider can help identify issues early.
Women, and those with a family history or other risk factors, should be vigilant about their reproductive health. They should discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider.
By combining lifestyle modifications with regular screenings and check-ups, women can significantly reduce their risk of developing uterine cancer.
Living with Uterine Cancer
Living with uterine cancer demands a holistic approach, encompassing medical treatment and emotional support. Patients face not just the physical challenges of the disease but also its emotional and psychological tolls.
Coping with Diagnosis and Treatment
Dealing with a uterine cancer diagnosis requires grasping the disease and its treatment choices. It’s vital for patients to be aware of the side effects from treatments like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
- Stay informed about the disease and treatment options.
- Maintain open communication with healthcare providers.
- Seek support from family, friends, and support groups.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Emotional and psychological support is essential for those living with uterine cancer. This support can originate from counseling, support groups, and loved ones.
Here are some ways to access emotional support:
- Professional counseling or therapy.
- Support groups for cancer patients.
- Online resources and forums.
Fertility and Sexual Health Considerations
Uterine cancer and its treatments can impact fertility and sexual health. Patients should discuss these concerns with their healthcare providers to understand their options and any necessary precautions.
Exploring fertility preservation options before treatment starts is a critical step for some patients.
The Future of Uterine Cancer Care and Research
The future of Uterine Cancer care looks bright, thanks to ongoing research and emerging trends. These advancements are aimed at improving patient outcomes. A better understanding of Uterine Cancer is being achieved through cancer research. This knowledge enables healthcare professionals to develop more effective treatment strategies.
Research into the genetic and molecular mechanisms of Uterine Cancer is driving the development of targeted therapies. These therapies are showing promise in clinical trials. Also, advancements in diagnostic techniques are leading to earlier detection and more accurate staging of the disease.
As Uterine Cancer research continues to evolve, patients can look forward to more personalized and effective treatments. Studies are exploring the use of immunotherapy and other innovative treatments. These efforts aim to improve outcomes for patients with Uterine Cancer.
FAQ About Uterine Cancer
Q: What is uterine cancer?
A: Uterine cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, starts in the uterus. It happens when cells in the uterus grow abnormally and spread to nearby tissues.
Q: What are the risk factors for uterine cancer?
A: Risk factors for uterine cancer include age and hormonal factors. Certain medical conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and obesity also increase risk. Family history of certain cancers and lifestyle choices play a role too.
Q: What are the symptoms of uterine cancer?
A: Symptoms include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and unusual vaginal discharge. Early signs can be mild and mistaken for other issues. It’s vital to seek medical help if symptoms persist.
Q: How is uterine cancer diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a physical exam, imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI, and biopsy. These steps help collect tissue samples for lab tests to check for cancer cells.
Q: What are the treatment options for uterine cancer?
A: Treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy. The choice depends on the cancer’s stage, grade, and the patient’s health.
Q: Can uterine cancer be prevented?
A: Preventing uterine cancer is challenging, but lifestyle changes can help. Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising, and managing medical conditions reduce risk. Regular screenings are key for early detection.
Q: What is the prognosis for uterine cancer?
A: Prognosis depends on the cancer’s stage, grade, and the patient’s health. Five-year survival rates vary. Early detection generally leads to a better prognosis.
Q: How does uterine cancer affect fertility and sexual health?
A: Uterine cancer and its treatment can impact fertility and sexual health. Surgery and radiation therapy can harm reproductive organs, leading to infertility or sexual function changes. It’s important to discuss these concerns with a healthcare provider.