What Is Vaginal Bleeding and Why It Occurs
Vaginal bleeding can be a source of concern and distress for many women. It’s a common gynecological issue that can happen at different stages of a woman’s life. It’s important to understand the causes and implications of this condition. While it’s a normal part of menstruation, it can also signal an underlying health issue that needs attention.
Women experiencing this symptom should be aware of the various factors that could be contributing to it. They should also know about the available treatment options. By delving into this topic, individuals can gain a better understanding of their bodies. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions about their health. Understanding vaginal bleeding is key for women’s health. It can signal a normal phase or an underlying issue. Vaginal bleeding is any bleeding outside of the regular menstrual period.
Definition and Basic Physiology
Vaginal bleeding can stem from various physiological or pathological causes. The female reproductive system is complex. It involves multiple organs and hormones to manage menstrual cycles.
The basic physiology of vaginal bleeding involves the shedding of the uterine lining, known as the endometrium. This happens when there’s no pregnancy. It’s a natural part of the menstrual cycle.
Normal vs. Abnormal Bleeding Patterns
It’s vital to distinguish between normal and abnormal vaginal bleeding to spot health issues. Normal menstrual bleeding lasts 3 to 7 days, with a cycle length of about 28 days.
Abnormal bleeding patterns include:
- Prolonged or heavy menstrual bleeding
- Intermenstrual bleeding between periods
- Postmenopausal bleeding
- Irregular cycles
These abnormal patterns can be due to hormonal imbalances, structural issues, or other medical conditions.
Common Causes of Vaginal Bleeding
Understanding the causes of vaginal bleeding is essential. It can arise from hormonal shifts, structural issues, or infections. Vaginal bleeding is a symptom influenced by various factors affecting the female reproductive system.
Hormonal Fluctuations
Hormonal changes are a frequent cause of vaginal bleeding. Shifts in estrogen and progesterone levels can disrupt regular bleeding patterns. These changes happen at different life stages, like puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause.
- Menstrual cycle irregularities due to hormonal imbalances
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) causing hormonal disturbances
- Thyroid disorders affecting menstrual regularity
Structural Abnormalities
Structural issues in the reproductive tract can also trigger vaginal bleeding. These problems include:
- Uterine fibroids, which are non-cancerous growths in the uterus
- Polyps in the cervix or uterus
- Endometriosis, where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus
These structural anomalies can result in irregular or heavy bleeding.
Infections and Inflammation
Infections and inflammatory conditions of the reproductive tract can also cause vaginal bleeding. Examples include:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Cervicitis, or inflammation of the cervix
- Vaginitis, or inflammation of the vagina
These conditions can lead to bleeding, often after intercourse or during menstruation.
Vaginal Bleeding During Reproductive Years
Understanding vaginal bleeding during the reproductive years is key to distinguishing normal from abnormal patterns. This life stage is marked by significant physiological changes. Vaginal bleeding can stem from various factors.

Menstrual Cycle Irregularities
Menstrual cycle irregularities are a common reason for vaginal bleeding in the reproductive years. Hormonal imbalances, stress, and certain medical conditions can disrupt menstrual cycles. These disruptions can result in changes in bleeding frequency, duration, or intensity.
Women experiencing irregularities may notice their bleeding patterns change. This could include heavier or lighter flow, or cycles that are longer or shorter. It’s vital for women to monitor their cycles to spot any deviations from the norm.
Ovulation Bleeding
Ovulation bleeding, or mid-cycle bleeding, happens in some women during ovulation. This bleeding is usually light and may come with mild pelvic pain. It’s generally seen as normal, but heavy or persistent bleeding warrants concern.
Contraceptive-Related Bleeding
Certain contraceptives can alter vaginal bleeding patterns. Hormonal contraceptives, for instance, may cause breakthrough bleeding or spotting, often in the first few months. While this bleeding is usually not a cause for alarm, it’s important for women to discuss any bleeding changes with their healthcare provider.
By grasping the causes and implications of vaginal bleeding in the reproductive years, women can better manage their reproductive health. They should seek medical help when necessary.
Pregnancy-Related Vaginal Bleeding
Bleeding during pregnancy is not uncommon, but it always requires careful evaluation. Vaginal bleeding can occur at any stage of pregnancy. It may be a normal variation or indicate a problem that needs medical attention.
First Trimester Bleeding
Bleeding during the first trimester affects up to 25% of women. It can be due to implantation, hormonal changes, or other factors. While some cases may signal complications, many women with first-trimester bleeding have normal pregnancies.
Second and Third Trimester Bleeding
Bleeding in the second and third trimesters is less common but more concerning. It could be due to placenta previa, placental abruption, or preterm labor. These conditions require immediate medical evaluation to ensure the health and safety of both mother and baby.
Postpartum Bleeding
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is a serious condition that can occur after childbirth, characterized by excessive bleeding. It is a leading cause of maternal morbidity and mortality worldwide. PPH can result from uterine atony, retained placental tissue, or lacerations during delivery. Prompt recognition and treatment are critical to managing postpartum bleeding effectively.
Understanding the causes and risks associated with pregnancy-related vaginal bleeding is essential for expectant mothers. While some bleeding may be benign, it’s critical to seek medical evaluation to rule out complications. By being informed and vigilant, pregnant women can help ensure a healthy pregnancy and postpartum experience.
Vaginal Bleeding in Perimenopause and Menopause
The transition to menopause, known as perimenopause, brings noticeable changes in vaginal bleeding. Women may see variations in menstrual cycle length and bleeding intensity. Understanding these changes is key for managing expectations and spotting any issues.
Perimenopausal Bleeding Patterns
Perimenopause is marked by hormonal fluctuations leading to irregular vaginal bleeding. Common patterns include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles, which may be longer or shorter than usual
- Variations in bleeding intensity, ranging from light spotting to heavy flows
- Occasional skipped periods
These changes can be unsettling. Yet, they are generally a normal part of the perimenopausal transition.
Postmenopausal Bleeding Concerns
Postmenopausal bleeding, occurring after menopause, is a significant concern. Any bleeding after menopause should prompt a healthcare provider’s evaluation. It can be a symptom of various conditions, some needing medical attention. Experts at Acıbadem International note that postmenopausal bleeding can stem from hormonal changes, infections, or serious conditions like cancer.
Key concerns with postmenopausal bleeding include:
- Endometrial atrophy or hyperplasia
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) side effects
- Gynecological cancers
Prompt medical evaluation is vital to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Medical Conditions Associated with Vaginal Bleeding
Vaginal bleeding can signal various health issues in women. It’s vital to identify these conditions for effective treatment.
Several health conditions can lead to vaginal bleeding. These include uterine fibroids, endometriosis and adenomyosis, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and thyroid disorders. Each condition has unique characteristics and impacts on women’s health differently.
Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths in or around the uterus. They are common in women of childbearing age. Symptoms include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure, and discomfort. Hormonal influences are believed to contribute to their development. Treatment depends on the fibroids’ size, location, and symptom severity.
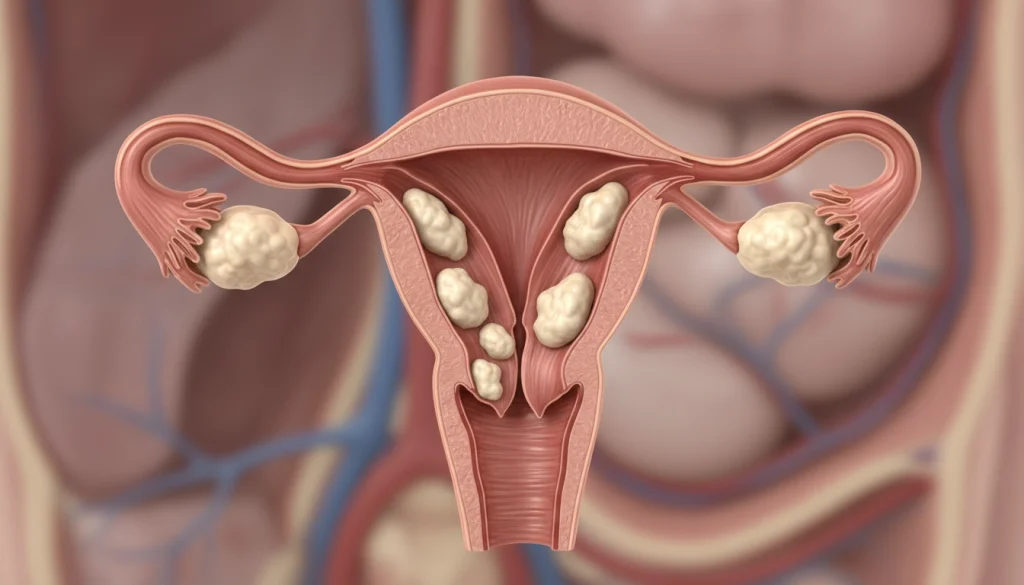
Endometriosis and Adenomyosis
Endometriosis involves tissue like the uterus lining growing outside the uterus, causing inflammation and scarring. Adenomyosis is similar but affects the uterus wall. Both can lead to painful periods, heavy bleeding, and infertility. Hormonal influences and genetic predisposition are thought to cause these conditions. Treatment includes hormonal therapies and surgery.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder affecting ovulation, leading to irregular cycles, ovarian cysts, and metabolic issues. It often causes irregular or prolonged menstrual bleeding due to hormonal imbalances. PCOS also increases the risk of diabetes and heart disease. Treatment involves hormonal therapies and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms and prevent long-term health risks. For more information on hormonal imbalances, visit this resource on estrogen levels.
Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can disrupt menstrual cycles and cause vaginal bleeding. The thyroid gland regulates metabolism and hormonal balance. Abnormal thyroid function can lead to irregular or heavy bleeding. Treatment focuses on managing thyroid hormone levels through medication and lifestyle adjustments.
These conditions show the complexity of vaginal bleeding as a symptom. Accurate diagnosis and treatment depend on understanding the underlying cause of the bleeding.
Potential Serious Causes of Vaginal Bleeding
Several serious health conditions can cause vaginal bleeding, highlighting the need for immediate medical evaluation. While many cases of vaginal bleeding are related to normal menstrual cycles or minor issues, some instances can indicate severe underlying health problems.
Gynecological Cancers
Gynecological cancers are among the serious causes of vaginal bleeding. These cancers can affect various parts of the female reproductive system.
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer often presents with abnormal vaginal bleeding, including bleeding after intercourse, between periods, or after menopause. Regular Pap smears are essential for early detection.
Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, typically causes irregular vaginal bleeding, often in postmenopausal women. Symptoms may also include pelvic pain and abnormal discharge.
Vaginal Cancer
Vaginal cancer is relatively rare but can cause vaginal bleeding, often after intercourse or pelvic exams. It is more common in older women and those with a history of cervical cancer or precancerous conditions.
Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in a fallopian tube. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and dizziness. Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage, or spontaneous abortion, is the loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week. Vaginal bleeding is a common symptom, ranging from light spotting to heavy bleeding. Other symptoms may include cramping and the passage of tissue.
The serious causes of vaginal bleeding underscore the importance of seeking medical care if bleeding is heavy, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for conditions like gynecological cancers, ectopic pregnancy, and miscarriage.
- Gynecological cancers can cause vaginal bleeding and require prompt medical evaluation.
- Ectopic pregnancy is a life-threatening condition that can cause vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain.
- Miscarriage is a common cause of vaginal bleeding during early pregnancy.
Diagnostic Approaches for Vaginal Bleeding
Diagnosing vaginal bleeding involves a range of medical assessments to pinpoint the cause. A detailed evaluation is essential for identifying the source of bleeding. This guides the appropriate treatment approach.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Starting with a detailed medical history and physical exam, healthcare providers gather vital information. They ask about menstrual history, previous pregnancies, and symptoms like pain or fever. A pelvic exam is performed to check the reproductive organs for any irregularities.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are critical in diagnosing vaginal bleeding. They include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) to check for anemia or infection
- Blood type and Rh factor, essential for pregnant women
- Pregnancy test to rule out pregnancy-related bleeding
- Hormone level assessments, such as thyroid function tests
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies are necessary to visualize the reproductive organs and identify structural abnormalities.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a primary imaging modality used to evaluate the uterus, ovaries, and other pelvic structures. It can identify conditions such as fibroids, cysts, or ectopic pregnancy.
MRI and CT Scans
In some cases, MRI or CT scans may be used to further evaluate the pelvic organs. This is when ultrasound findings are inconclusive or when assessing for more complex conditions.
Treatment Options for Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding
The treatment for abnormal vaginal bleeding hinges on identifying the root cause. Effective management can greatly enhance one’s quality of life.
Medications
Medications are key in managing abnormal vaginal bleeding. The choice of treatment is often based on the underlying cause.
Hormonal Treatments
Hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills and hormonal IUDs, are frequently used. They help regulate menstrual cycles and decrease bleeding.
Non-Hormonal Options
For those where hormonal treatments are not suitable, non-hormonal medications like tranexamic acid can be effective. They help reduce heavy menstrual bleeding.

Surgical Interventions
When conservative management fails or is not suitable, surgical options may be considered.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Procedures like endometrial ablation aim to reduce or stop bleeding. They target the lining of the uterus.
Major Surgical Options
In some cases, more extensive surgeries like hysterectomy may be necessary. This is often for conditions like uterine fibroids or certain cancers.
Alternative Therapies
Some women may explore alternative therapies, including acupuncture and herbal supplements. Yet, evidence supporting their effectiveness for abnormal vaginal bleeding is limited.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Vaginal Bleeding
Recognizing the signs that indicate the need for immediate medical evaluation for vaginal bleeding is vital. This symptom can signal a range of conditions, from minor to severe health issues. It’s essential to understand when to seek help to ensure your reproductive health remains intact and any problems are addressed promptly.
Emergency Warning Signs
Certain symptoms that accompany vaginal bleeding require immediate medical attention. These emergency warning signs include:
- Heavy bleeding that soaks through one or more sanitary pads or tampons per hour
- Severe abdominal pain or cramping
- Dizziness or fainting
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Fever above 100.4°F (38°C)
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s critical to seek emergency medical care.
Non-Emergency Situations Requiring Medical Evaluation
Even without emergency warning signs, certain situations require a medical evaluation. These include:
- Prolonged or irregular vaginal bleeding
- Bleeding between periods or after intercourse
- Postmenopausal bleeding
- Bleeding accompanied by other symptoms like pelvic pain or unusual discharge
Consulting a healthcare provider in these situations can help determine the cause of the bleeding and appropriate treatment options. Regular check-ups and open communication with your healthcare provider are key to managing your reproductive health.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Adopting a healthy lifestyle and regular gynecological check-ups are vital for preventing and managing vaginal bleeding. Simple changes in daily routines can help reduce abnormal vaginal bleeding. This approach is key to maintaining reproductive health.
Lifestyle Modifications
Healthy lifestyle choices greatly impact reproductive health. This includes dietary changes, regular physical activity, and effective stress management. These habits are essential for overall well-being.
Diet and Exercise
A balanced diet and regular exercise are critical for hormonal balance and reproductive health. Key dietary recommendations include:
- Increasing intake of iron-rich foods to prevent anemia
- Consuming foods high in omega-3 fatty acids for their anti-inflammatory properties
- Maintaining adequate hydration
Regular physical activity, such as walking or yoga, also contributes to overall well-being.
Stress Management
High stress levels can worsen hormonal imbalances, potentially leading to vaginal bleeding. Effective stress management techniques include:
- Meditation and mindfulness practices
- Deep breathing exercises
- Engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy
Regular Gynecological Check-ups
Regular visits to a gynecologist are essential for maintaining reproductive health and early detection of issues. During these check-ups, healthcare providers can:
- Perform routine screenings and examinations
- Discuss any changes in menstrual cycle or vaginal bleeding patterns
- Provide guidance on maintaining reproductive health
Psychological Impact of Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding
The psychological effects of vaginal bleeding are often ignored, yet they are vital to a woman’s well-being. Abnormal bleeding can cause anxiety, uncertainty, and distress. These feelings can disrupt daily life and strain relationships.
Coping with Uncertainty and Anxiety
Dealing with the uncertainty and anxiety from abnormal vaginal bleeding requires a broad strategy. Women can find relief through stress management techniques. Activities like meditation and deep breathing exercises can help reduce anxiety levels.
Support Resources
Support is key for women facing the psychological toll of vaginal bleeding. Resources include counseling services, support groups, and online forums. These platforms allow women to share their stories and connect with others who understand their struggles.
Moving Forward: Managing Your Gynecological Health
Understanding vaginal bleeding and its causes is key to good gynecological health. Recognizing normal versus abnormal bleeding patterns is essential. This knowledge empowers individuals to address any health issues promptly.
Effective management of vaginal bleeding requires lifestyle changes and regular health check-ups. A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and exercise, can lower the risk of abnormal bleeding. These habits are foundational for maintaining gynecological health.
Seeking medical help when needed is critical. Symptoms like heavy or prolonged bleeding, severe pain, or bleeding between periods need immediate attention. Being aware of these signs and acting swiftly is vital for protecting one’s health.
Staying informed and proactive is essential for managing gynecological health. Regular health consultations with a provider offer personalized advice and support. This approach helps in maintaining optimal reproductive health and reducing complications from vaginal bleeding.
FAQ
Q: What is vaginal bleeding?
A: Vaginal bleeding is any blood loss outside of a woman’s regular menstrual cycle. This includes spotting, heavy bleeding, or prolonged bleeding.
Q: What are the common causes of vaginal bleeding?
A: Common causes include hormonal changes, structural issues, infections, and certain medical conditions. These include uterine fibroids, endometriosis, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Q: Is vaginal bleeding during pregnancy a concern?
A: Yes, it is a concern during pregnancy. It may signal issues like miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or placenta previa. If you experience bleeding, seek medical help right away.
Q: How is vaginal bleeding diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a medical history, physical exam, and lab tests. Imaging studies like ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans are also used to find the cause.
Q: What are the treatment options for abnormal vaginal bleeding?
A: Treatment varies based on the cause. It may include medications, surgical options, or alternative therapies.
Q: When should I seek medical attention for vaginal bleeding?
A: Seek immediate medical help for heavy bleeding, severe pain, or emergency signs. For persistent or irregular bleeding, a medical evaluation is necessary.
Q: Can lifestyle modifications help manage vaginal bleeding?
A: Yes, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help manage vaginal bleeding and reproductive health.
Q: What is the psychological impact of abnormal vaginal bleeding?
A: It can cause uncertainty, anxiety, and emotional distress. There are coping strategies and support resources available to help manage these effects.
Q: How can I manage my gynecological health?
A: Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and staying informed about reproductive health can help manage gynecological health. This reduces the risk of abnormal vaginal bleeding.